Recombinant Mouse IFN-gamma/IFNG protein (His Tag)
种属
Mouse
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse IFN-gamma protein His23-Cys155 (Accession# P01580) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 15978 |
| 蛋白编号 | P01580 |
| 预测分子量 | 19.3 kDa |
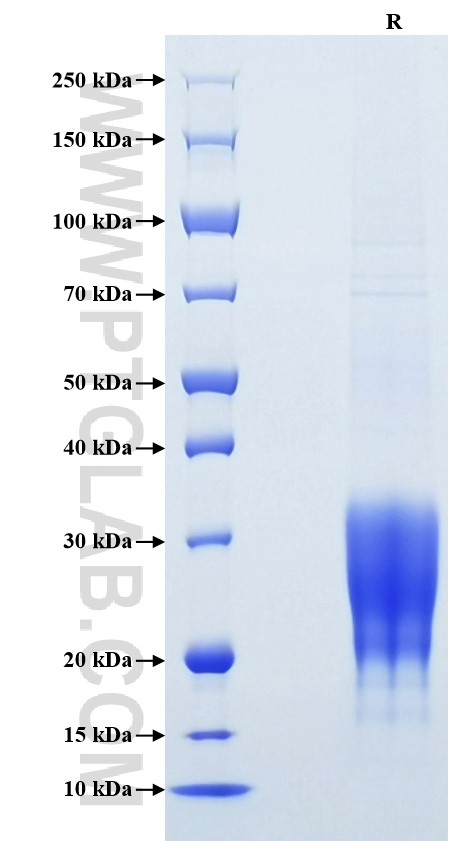
| SDS-PAGE | 20-35 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
The IFNs were originally discovered as agents that interfere with viral replication. Initially, they were classified by the secreting cell type but are now classified into type I and type II according to receptor specificity and sequence homology. Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. It is secreted by Th1 cells, cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. The cytokine is associated with antiviral, immunoregulatory and anti-tumor properties and is a potent activator of macrophages. It plays crucial roles in pathogen clearance. Aberrant Ifng expression is associated with a number of autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases. It has been identified in many studies as a biomarker for pleural tuberculosis (TB). Mutations in this gene are associated with aplastic anemia.
参考文献:
1. Isaacs, A. et al.(1957). The interferon Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 147: 258-267. 2. Gray PW. et al. (1982). Nature. 298 : 859-63. 3. Bullens, D. M. et al.(2001). Int. Immunol. 13: 181-191. 4. Wang Z. et al.(2014). Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.78: 588-92. 5. Chegou NN. et al.(2012). PLoS One.7(6):e38501