验证数据展示
产品信息
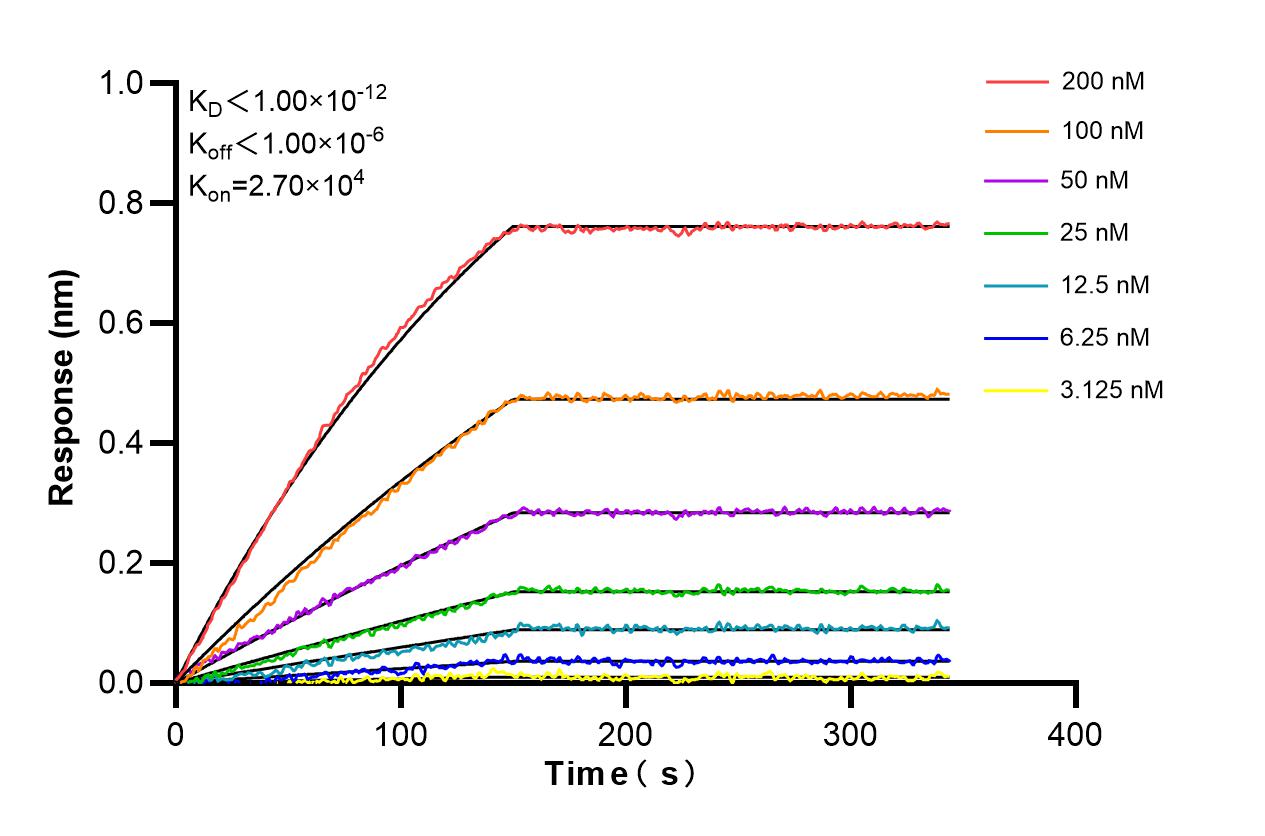
86044-1-PBS targets iASPP as part of a matched antibody pair:
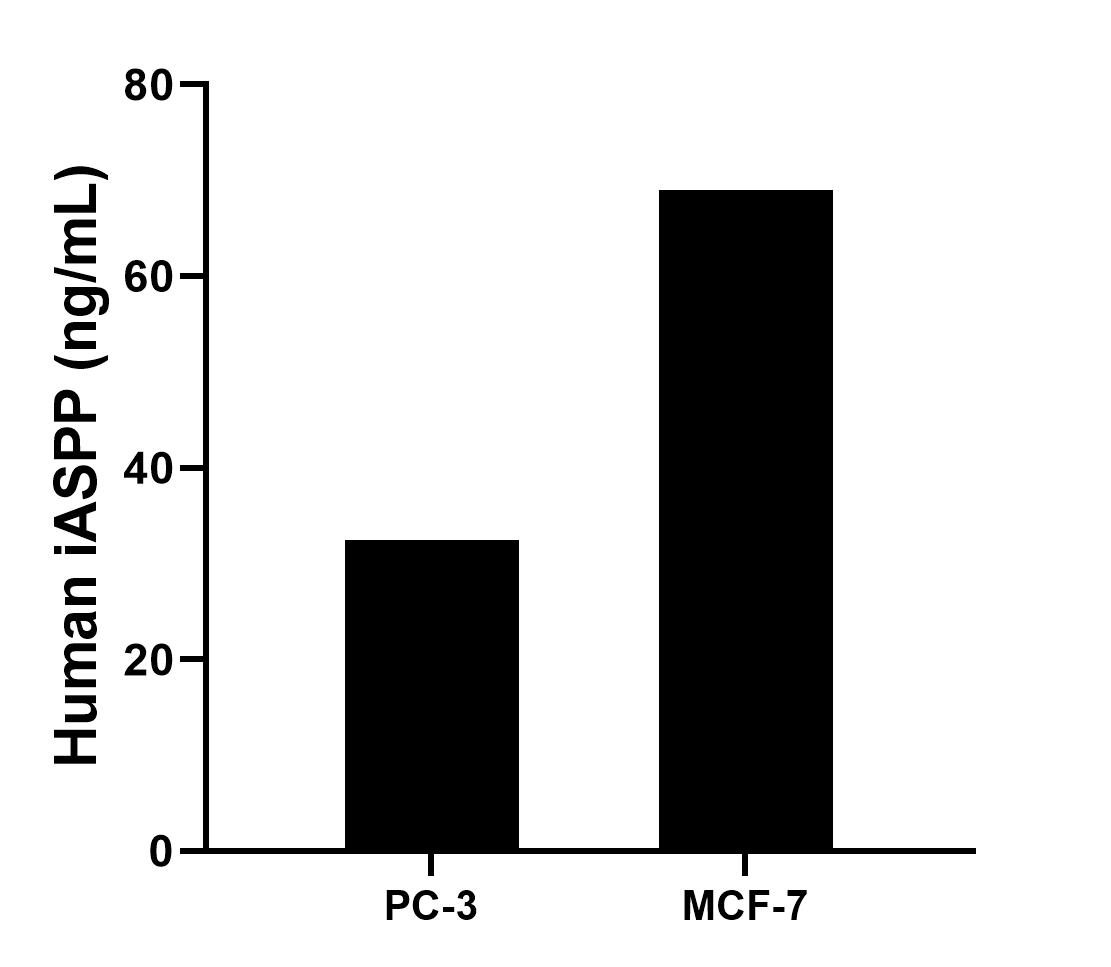
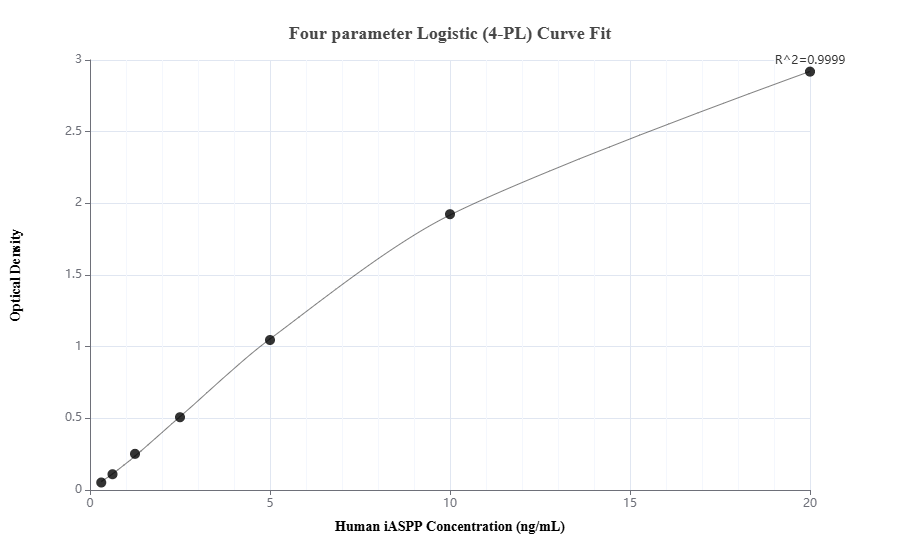
MP02334-1: 86044-3-PBS capture and 86044-1-PBS detection (validated in Sandwich ELISA)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| 经测试应用 | WB, Sandwich ELISA, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse |
| 免疫原 |
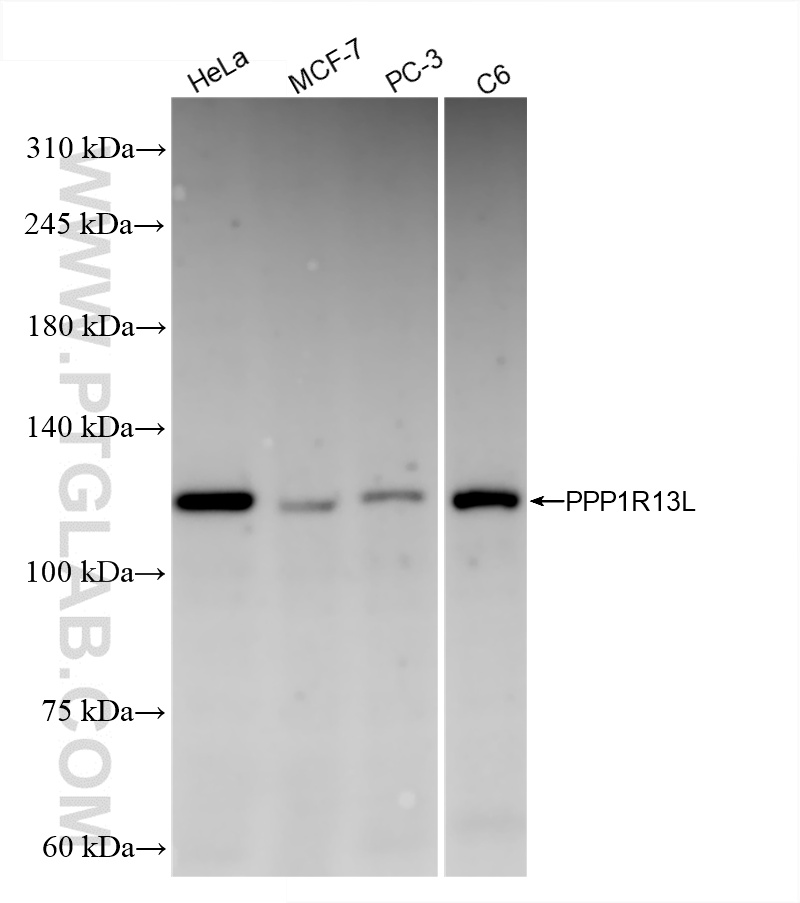
CatNo: Ag13273 Product name: Recombinant human PPP1R13L protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 481-829 aa of BC064913 Sequence: EGPVARPLSPTRLQPALPPEAQSVPELEEVARVLAEIPRPLKRRGSMEQAPAVALPPTHKKQYQQIISRLFHRHGGPGPGGPEPELSPITEGSEARAGPPAPAPPAPIPPPAPSQSSPPEQPQSMEMRSVLRKAGSPRKARRARLNPLVLLLDAALTGELEVVQQAVKEMNDPSQPNEEGITALHNAICGANYSIVDFLITAGANVNSPDSHGWTPLHCAASCNDTVICMALVQHGAAIFATTLSDGATAFEKCDPYREGYADCATYLADVEQSMGLMNSGAVYALWDYSAEFGDELSFREGESVTVLRRDGPEETDWWWAALHGQEGYVPRNYFGLFPRVKPQRSKV 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Recombinant |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 13 like |
| 别名 | PPP1R13L, Inhibitor of ASPP protein, NFkB-interacting protein 1, NKIP1, PPP1R13B like protein |
| 计算分子量 | 89 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 110 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC064913 |
| 基因名称 | PPP1R13L |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10848 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q8WUF5 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (iASPP), encoded by PPP1R13L gene, is often overexpressed in human cancers. The ASPP family includes three members, namely ASPP1, ASPP2, and iASPP, which are specific regulators of p53-, p63-, and p73-mediated apoptosis. ASPP1 and ASPP2 enhance the apoptotic function of p53, whereas iASPP specifically inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis. Overexpression of iASPP is associated with resistance to cisplatin-induced apoptosis and rediation therapy. iASPP plays a pivotal role in regulating cancer cell proliferation and tumor progression.