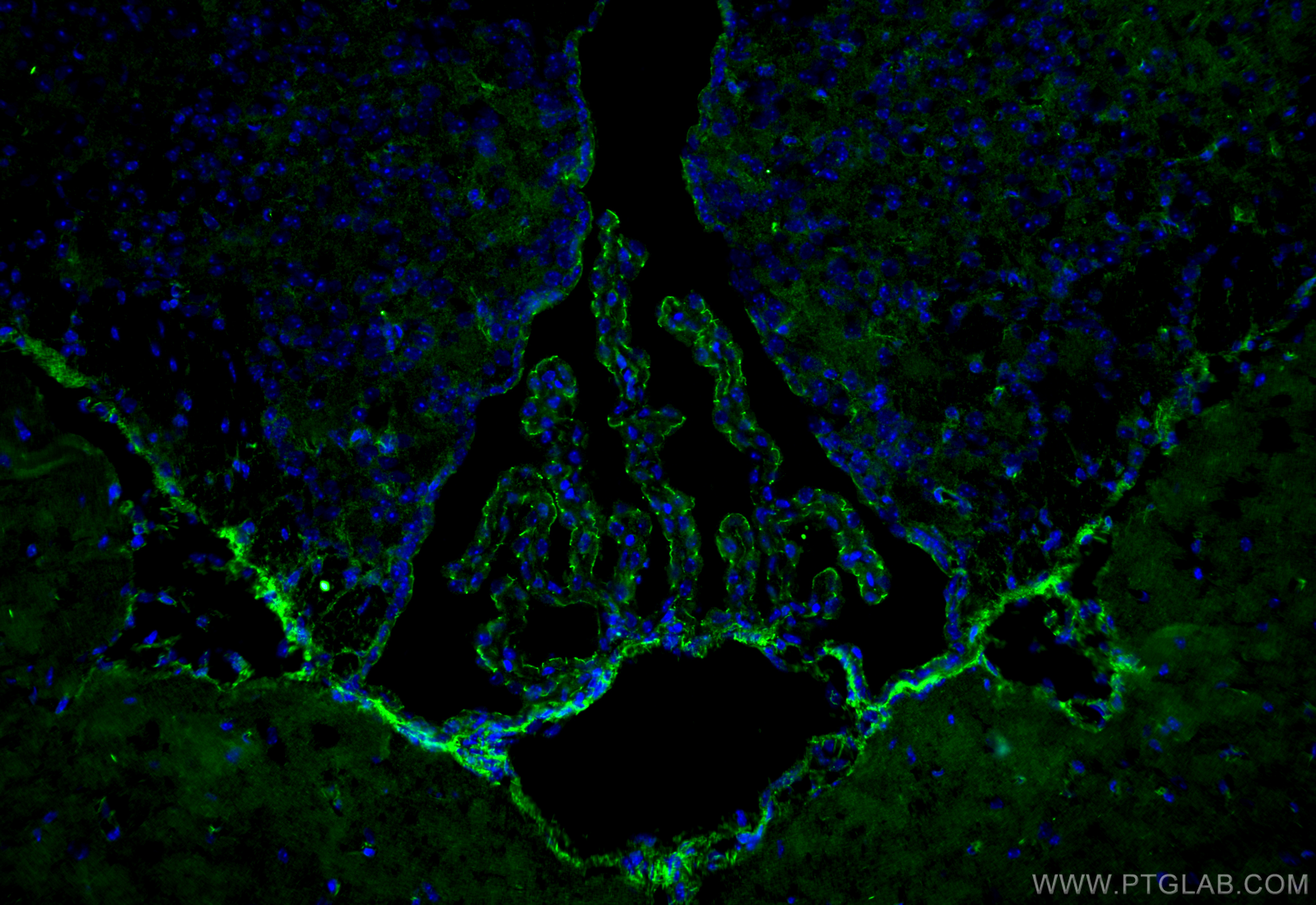
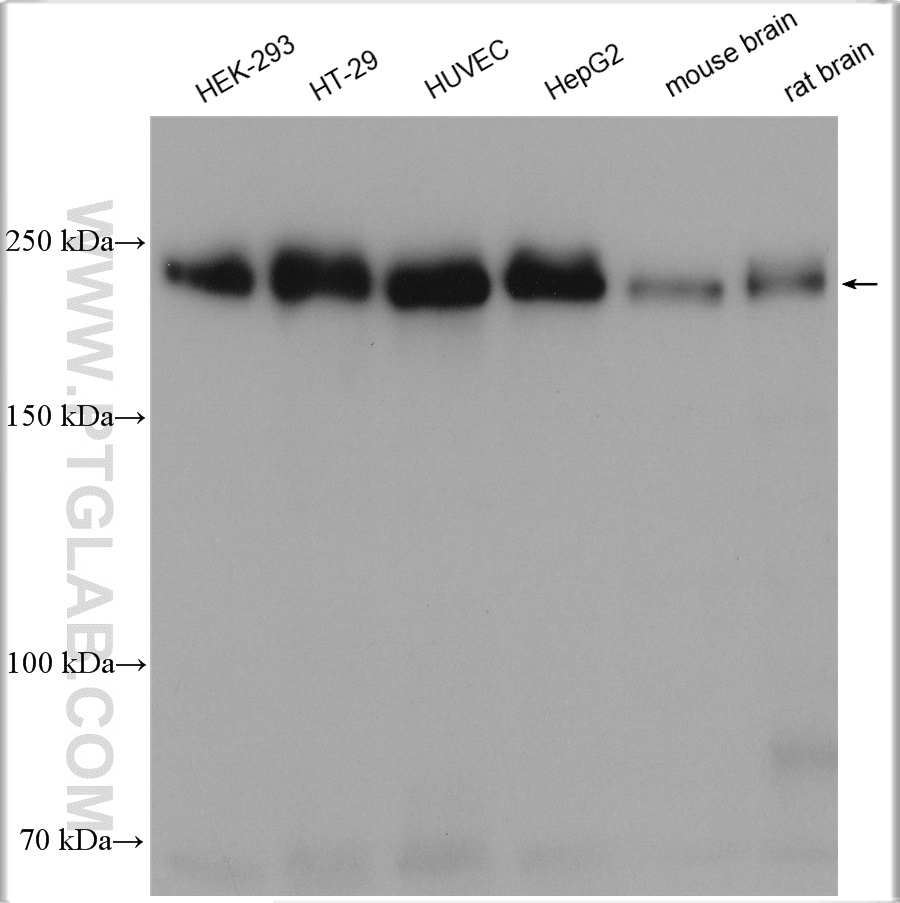
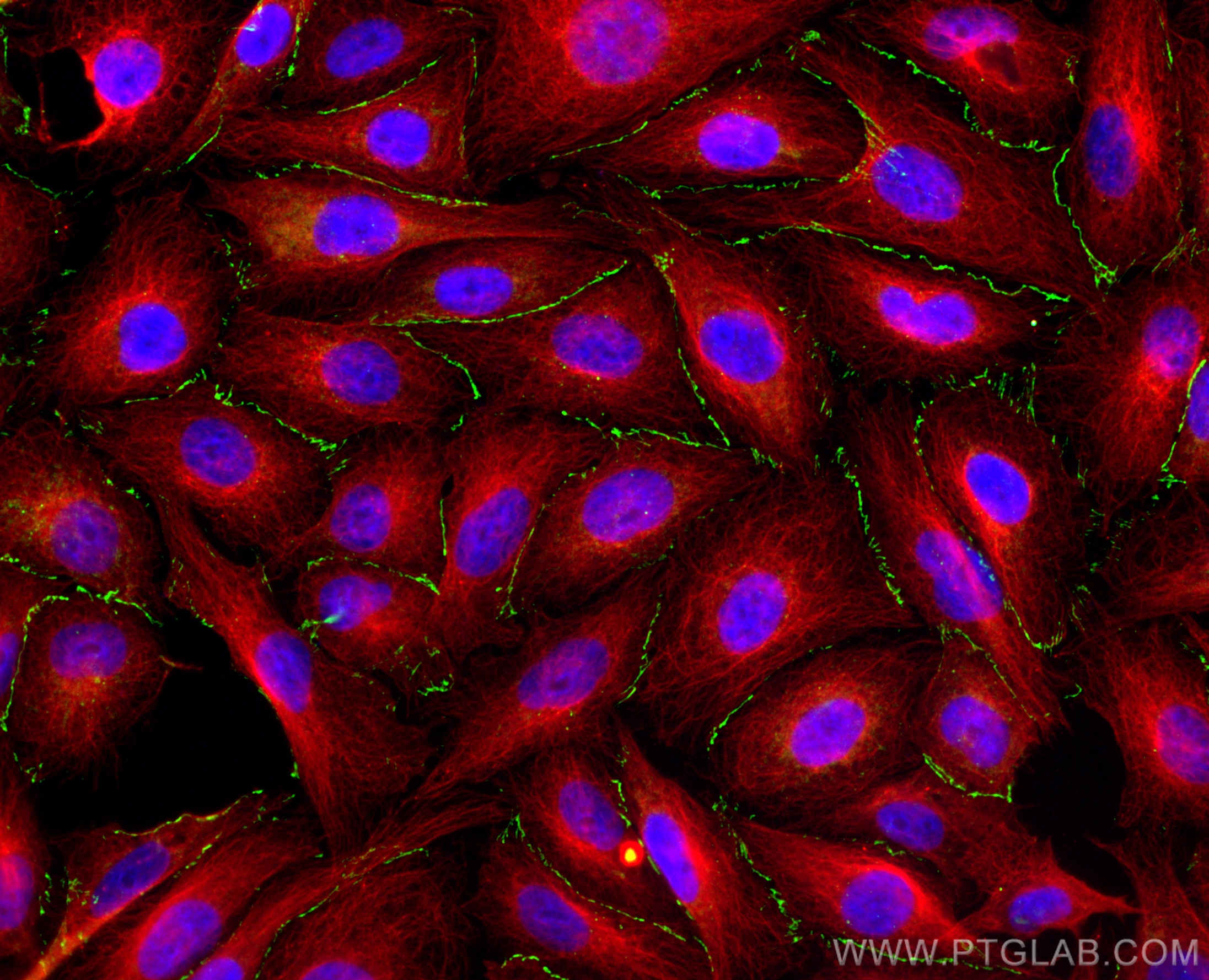
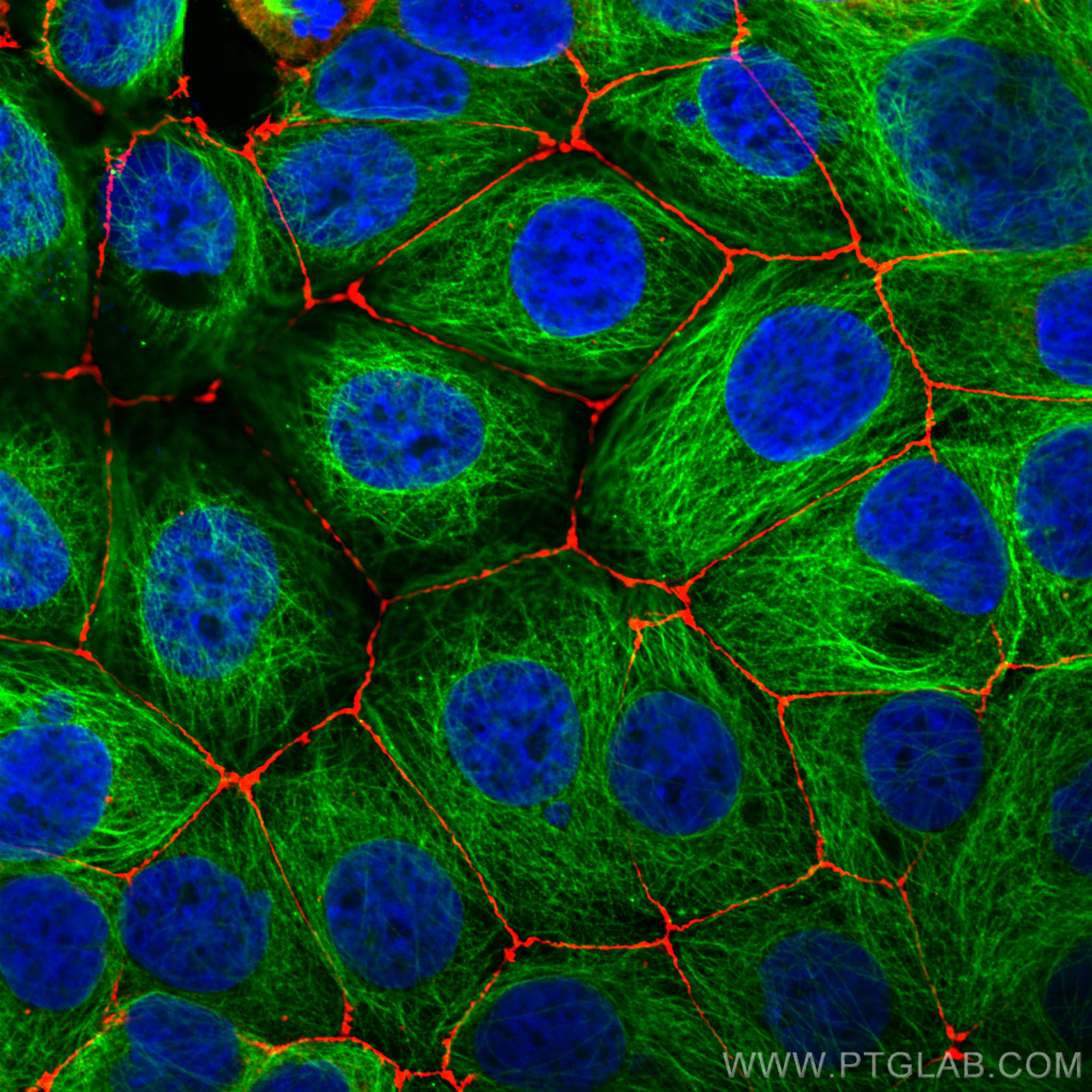
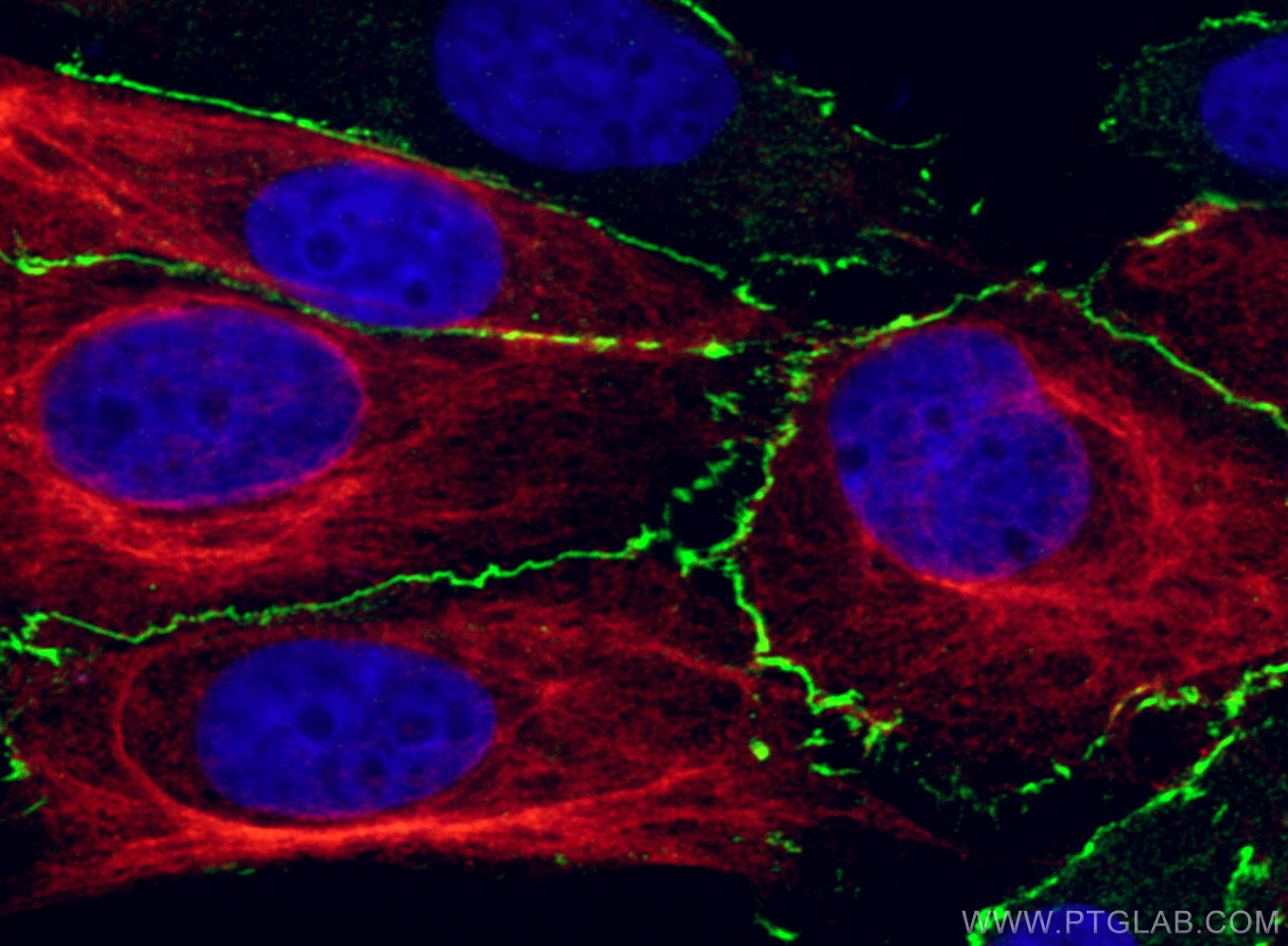
验证数据展示
发表文章中的应用
| WB | See 1 publications below |
产品信息
21773-1-PBS targets ZO-1 in WB, IF/ICC, IF-Fro, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster samples.
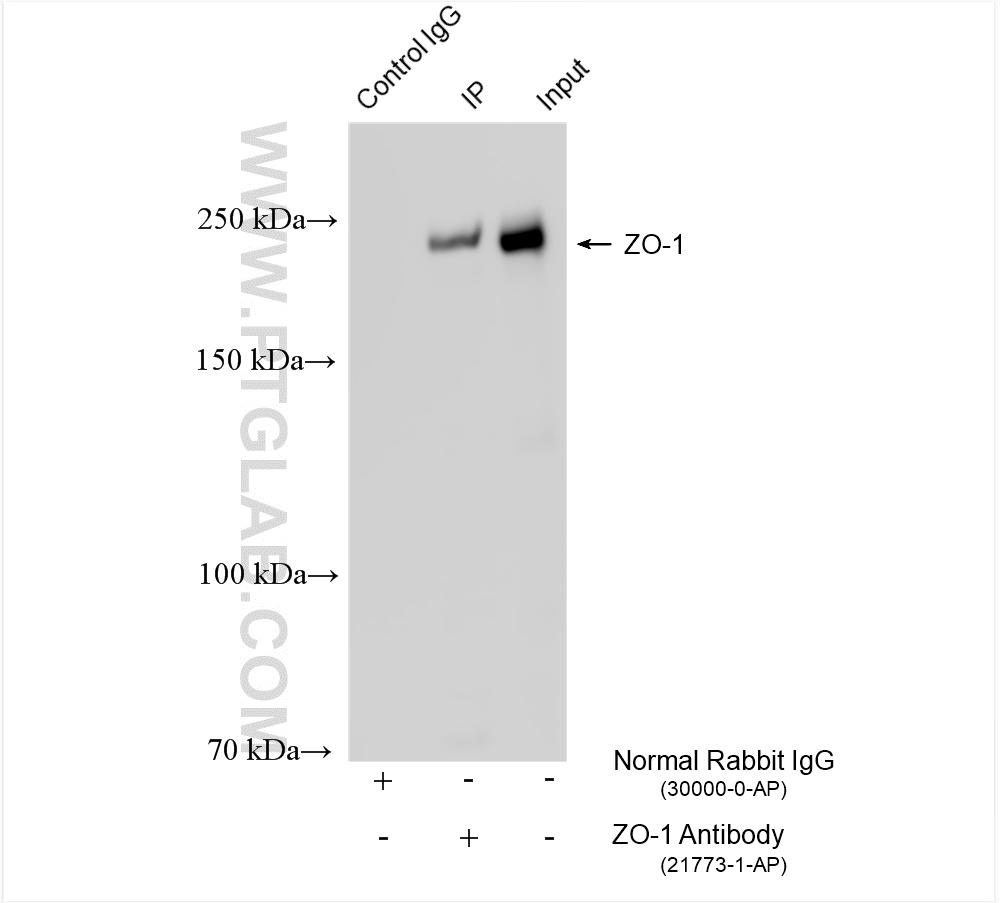
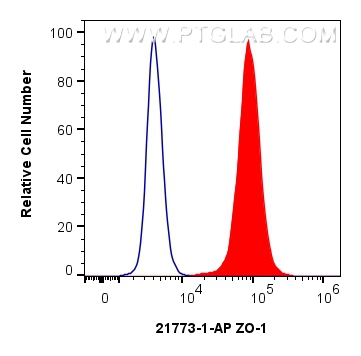
| 经测试应用 | WB, IF/ICC, IF-Fro, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat, canine, hamster |
| 文献引用反应性 | mouse |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag16454 Product name: Recombinant human ZO1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1446-1748 aa of BC111712 Sequence: SLHIHSKGAHGEGNSVSLDFQNSLVSKPDPPPSQNKPATFRPPNREDTAQAAFYPQKSFPDKAPVNGTEQTQKTVTPAYNRFTPKPYTSSARPFERKFESPKFNHNLLPSETAHKPDLSSKTPTSPKTLVKSHSLAQPPEFDSGVETFSIHAEKPKYQINNISTVPKAIPVSPSAVEEDEDEDGHTVVATARGIFNSNGGVLSSIETGVSIIIPQGAIPEGVEQEIYFKVCRDNSILPPLDKEKGETLLSPLVMCGPHGLKFLKPVELRLPHCDPKTWQNKCLPGDPNYLVGANCVSVLIDHF 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) |
| 别名 | TJP1, Tight junction protein 1, Tight junction protein ZO 1, Tight junction protein ZO-1, ZO 1 |
| 计算分子量 | 1748 aa, 195 kDa |
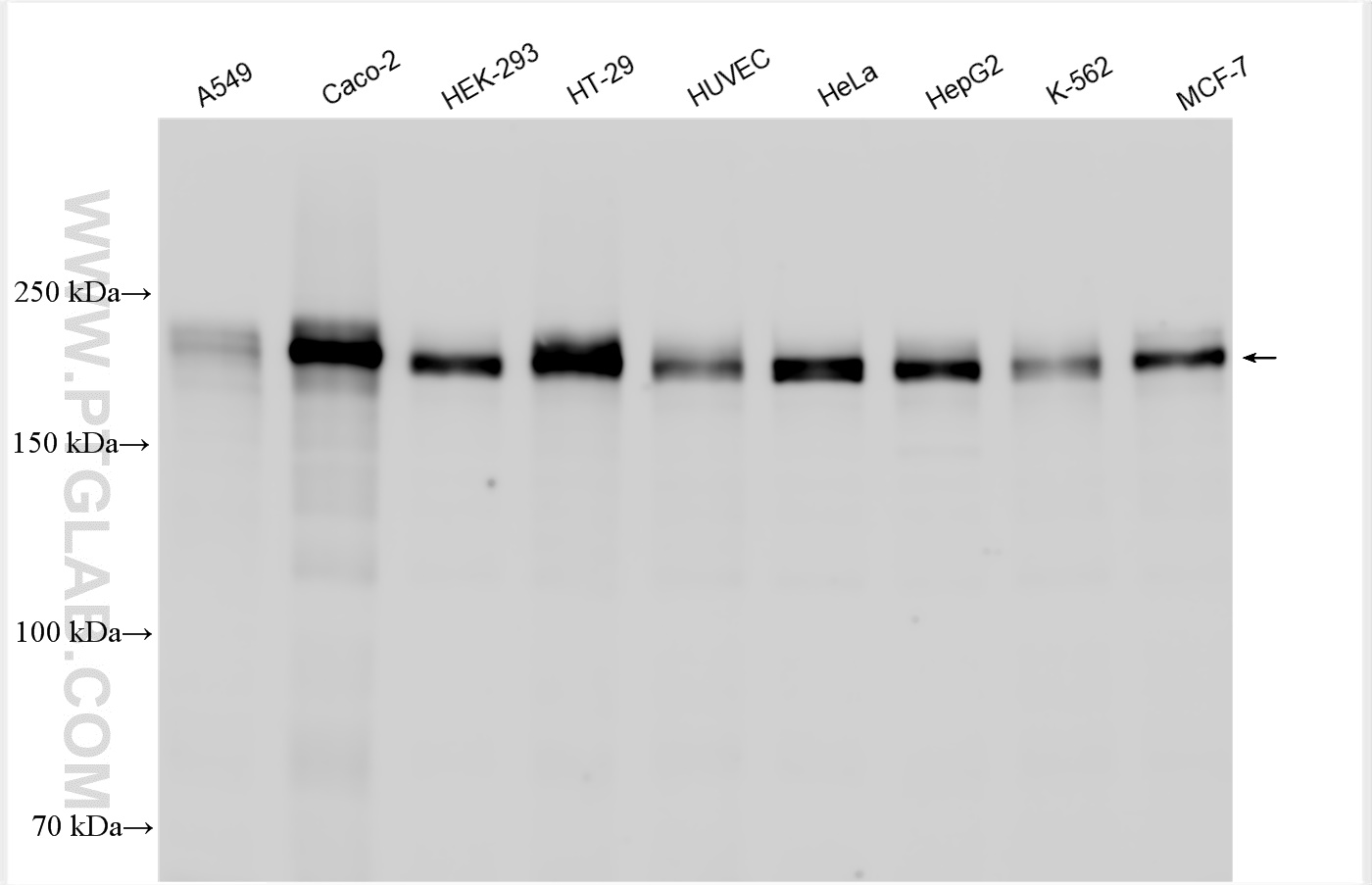
| 观测分子量 | 230 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC111712 |
| 基因名称 | ZO-1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7082 |
| RRID | AB_10733242 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q07157 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
What is the function of ZO-1?
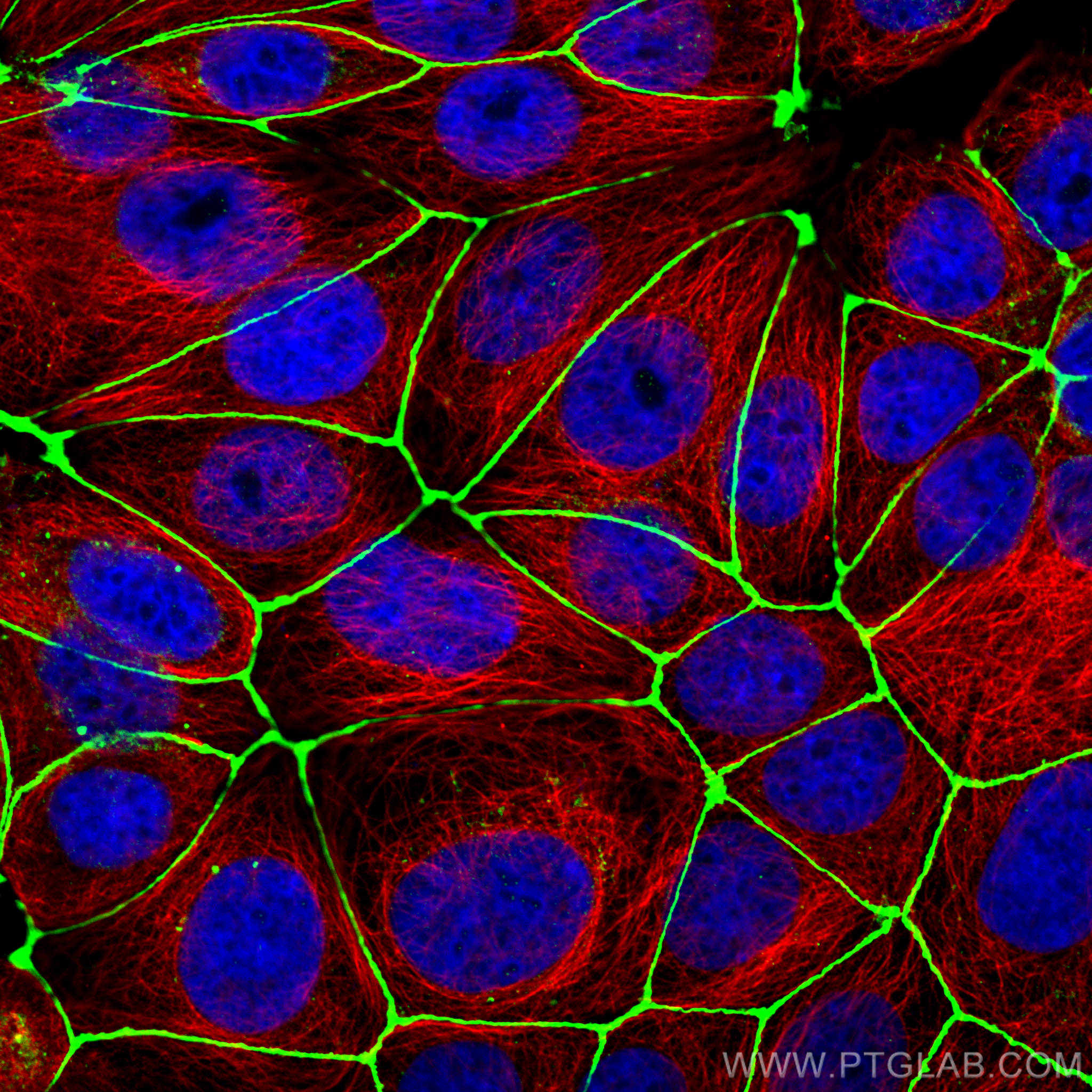
Zona Occludens 1 (ZO-1) is a tight junction (TJ) protein found in complexes at cell-cell contacts. The role of ZO-1 is to recruit other TJ proteins.1,2 The resulting TJ complexes regulate paracellular flow, contribute to apical-basal polarity, and are part of signaling pathways for proliferation and differentiation.3 This protein is useful for highlighting cell-cell contacts both in cultured cells and in tissue samples, outlining cell membranes and specific structures.
Where is ZO-1 expressed?
The protein is localized to the cytoplasmic membrane in most types of cells, particularly where a barrier function is essential. It is common in endothelial cells,4 which line the internal surface of blood and lymph vessels, and in epithelial cells,5 which form the outer barrier of organs.
ZO-1 is expressed in many tissues including the intestine, kidney, liver, and skeletal muscle cells.
What proteins does ZO-1 interact with?
ZO-1 contains multiple distinct protein domains that allow bind to other junctional proteins at the cytoplasmic membrane. The N-terminal of ZO-1 can dimerize with other ZO proteins and bind directly to other TJ proteins including claudins, connexions, and JAMs,6-10 which allows it to assemble TJ complexes. The C-terminal can interact with actin and cortactin, anchoring the TJ complexes to the cytoskeleton.8,11 This suggests that ZO-1 forms a link between the outer cell-cell contacts and the inner actin.
What is the molecular weight of ZO-1?
ZO-1 has an apparent molecular weight of 210-225 kDa. There are two isoforms of ZO-1, α+ and α-, which are produced by alternative RNA splicing and differ in the presence or absence of an internal 80-amino acid domain12,13. In some literature, the bands with a molecular weight of 250-260 kDa can also be detected for ZO-114,15,16,17.
1. McNeil, E., Capaldo, C. T. & Macara, I. G. Zonula occludens-1 function in the assembly of tight junctions in Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 1922-32 (2006).
2. Kratzer, I. et al. Complexity and developmental changes in the expression pattern of claudins at the blood-CSF barrier. Histochem. Cell Biol. (2012). doi:10.1007/s00418-012-1001-9
3. Guillemot, L., Paschoud, S., Pulimeno, P., Foglia, A. & Citi, S. The cytoplasmic plaque of tight junctions: A scaffolding and signalling center. Biochim. Biophys. Acta - Biomembr. 1778, 601-613 (2008).
4. Tornavaca, O. et al. ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J. Cell Biol. 208, 821-38 (2015).
5. Umeda, K. et al. Establishment and characterization of cultured epithelial cells lacking expression of ZO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 44785-94 (2004).
6. Stevenson, B. R. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J. Cell Biol. 103, 755-766 (1986).
7. Itoh, M. et al. Direct Binding of Three Tight Junction-Associated Maguks, Zo-1, Zo-2, and Zo-3, with the Cooh Termini of Claudins. J. Cell Biol. 147, 1351-1363 (1999).
8. Fanning, A. S., Jameson, B. J., Jesaitis, L. A. & Anderson, J. M. The Tight Junction Protein ZO-1 Establishes a Link between the Transmembrane Protein Occludin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29745-29753 (1998).
9. Kausalya, P. J., Reichert, M. & Hunziker, W. Connexin45 directly binds to ZO-1 and localizes to the tight junction region in epithelial MDCK cells. FEBS Lett. 505, 92-96 (2001).
10. Itoh, M. et al. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3. J. Cell Biol. 154, 491-498 (2001).
11. Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A., Moroi, S. & Tsukita, S. Involvement of ZO-1 in Cadherin-based Cell Adhesion through Its Direct Binding to α Catenin and Actin Filaments. J. Cell Biol. 138, 181-192 (1997).
12. Balda MS, Anderson JM. Two classes of tight junctions are revealed by ZO-1 isoforms. Am J Physiol. 264, (4 Pt 1):C918-24 (1993).
13. Sheth B, Fesenko I, Collins JE, Moran B, Wild AE, Anderson JM, Fleming TP. Tight junction assembly during mouse blastocyst formation is regulated by late expression of ZO-1 alpha+ isoform. Development. 124, (10):2027-37(1997).
14. Lassiter R, Merchen TD, Fang X, Wang Y. Protective Role of Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase in Allograft Rejection and Tubular Injury in Kidney Transplantation. Front Immunol. 7, 12:671025 (2021).
15. Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Soldner ELB, Sokola BS, Alluri SR, Abner EL, Kryscio RJ, Pekcec A, Schlichtiger J, Bauer B. Matrix Metalloproteinase-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in Epilepsy. J Neurosci. 2, 38(18):4301-4315 (2018).
16. Lin SC, Way EL. Effects of morphine and B-endorphin on Ca2+-ATPase activity of synaptic plasma membranes. NIDA Res Monogr. 75, 117-20(1986).
17. Wu Z, Mirza H, Teo JD, Tan KS. Strain-dependent induction of human enterocyte apoptosis by blastocystis disrupts epithelial barrier and ZO-1 organization in a caspase 3- and 9-dependent manner. Biomed Res Int. 2014, 209163(2014).