验证数据展示
产品信息
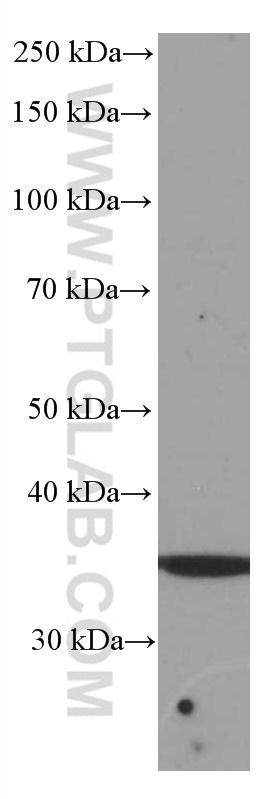
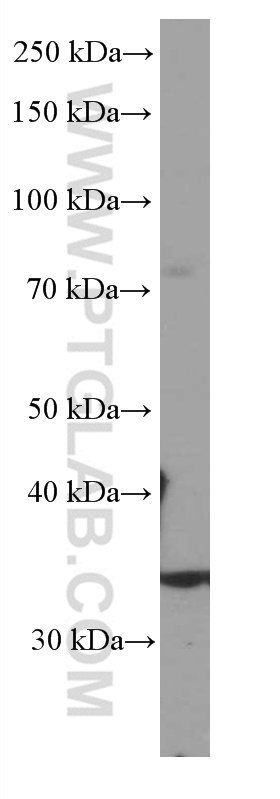
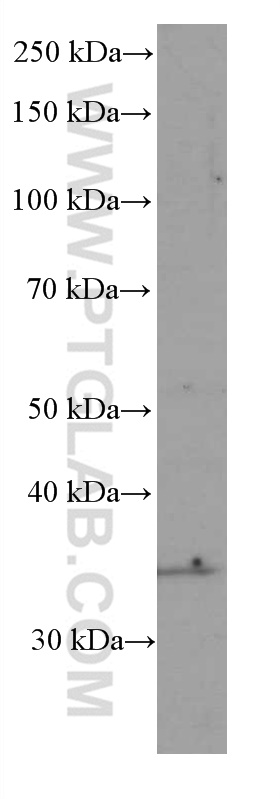
66543-1-PBS targets SIRT4 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag17347 Product name: Recombinant human SIRT4 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-314 aa of BC109319 Sequence: MKMSFALTFRSAKGRWIANPSQPCSKASIGLFVPASPPLDPEKVKELQRFITLSKRLLVMTGAGISTESGIPDYRSEKVGLYARTDRRPIQHGDFVRSAPIRQRYWARNFVGWPQFSSHQPNPAHWALSTWEKLGKLYWLVTQNVDALHTKAGSRRLTELHGCMDRVLCLDCGEQTPRGVLQERFQVLNPTWSAEAHGLAPDGDVFLSEEQVRSFQVPTCVQCGGHLKPDVVFFGDTVNPDKVDFVHKRVKEADSLLVVGSSLQVYSGYRFILTAWEKKLPIAILNIGPTRSDDLACLKLNSRCGELLPLIDPC 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG1 |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | sirtuin (silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog) 4 (S. cerevisiae) |
| 别名 | EC:2.3.1.-, EC:2.3.1.286, EC:2.4.2.-, NAD-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase sirtuin-4, NAD-dependent protein biotinylase sirtuin-4 |
| 计算分子量 | 314 aa, 35 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 35 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC109319 |
| 基因名称 | SIRT4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 23409 |
| RRID | AB_2881905 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9Y6E7 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
SIRT4, also named as NAD-dependent protein lipoamidase sirtuin-4, mitochondria, is a 314 amino acid protein, which belongs to the sirtuin family. Class II subfamily. SIRT4 is detected in vascular smooth muscle and striated muscle. SIRT4 is detected in insulin-producing beta-cells in pancreas islets of Langerhans. SIRT4 Acts as NAD-dependent protein lipoamidase, ADP-ribosyl transferase and deacetylase. It catalyzes more efficiently removal of lipoyl- and biotinyl- than acetyl-lysine modifications and inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDH) activity via the enzymatic hydrolysis of the lipoamide cofactor from the E2 component, DLAT, in a phosphorylation-independent manner. SIRT4 expression is down-regulated in a number of cancers, while overexpression reduces cell proliferation, transformation, and tumor development.