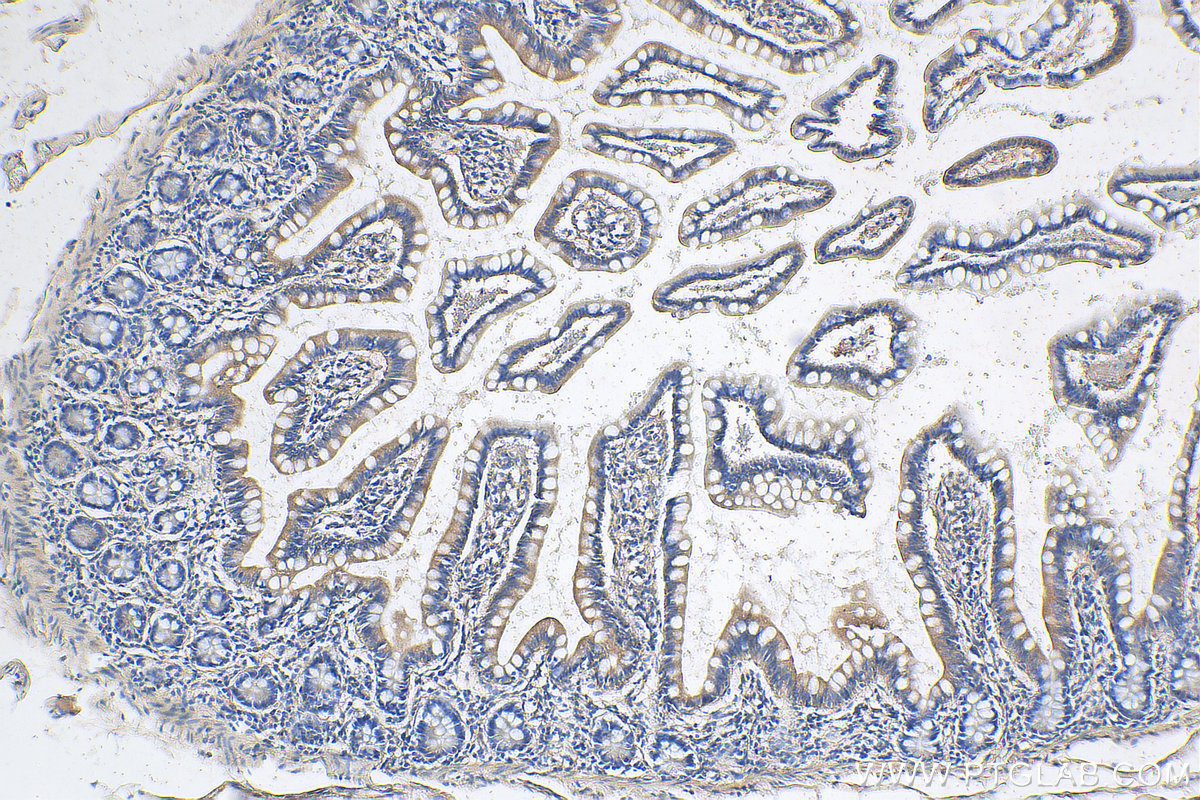
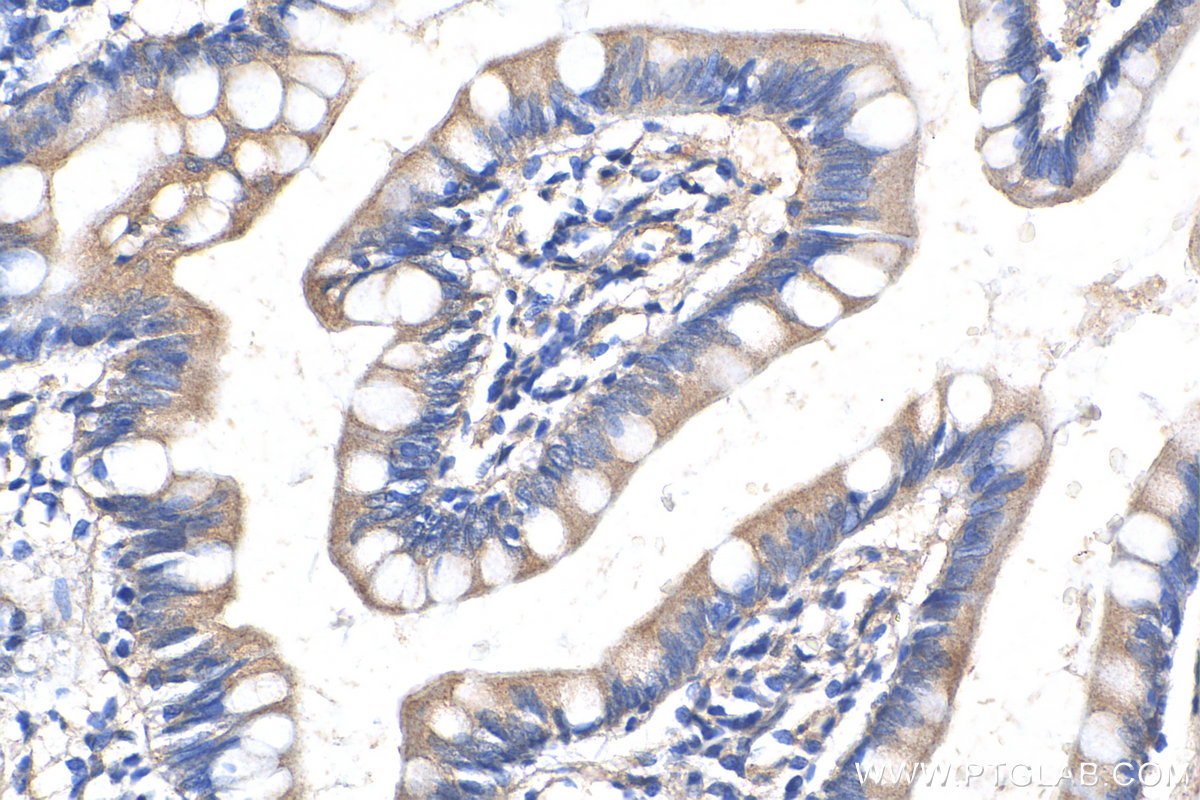
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive IHC detected in | human small intestine tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
18232-1-AP targets RETNLB in IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | IHC, ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag12912 Product name: Recombinant human RETNLB protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 22-111 aa of BC069318 Sequence: STQCSLDSVMDKKIKDVLNSLEYSPSPISKKLSCASVKSQGRPSSCPAGMAVTGCACGYGCGSWDVQLETTCHCQCSVVDWTTARCCHLT 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | resistin like beta |
| 别名 | CCRG, FIZZ1, FIZZ2, HXCP2, RELM beta, RELMb, RELMbeta, resistin like beta, RETNL2, RETNLB, XCP2 |
| 计算分子量 | 111 aa, 12 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC069318 |
| 基因名称 | RETNLB |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 84666 |
| RRID | AB_2935447 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9BQ08 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
RETNLB is an intestinal goblet cell-specific protein and is notably upregulated during intestinal inflammation. RETNLB also plays a role in several research areas, such as inflammatory disease, cancer, and metabolic function. In tumors, previous reports have suggested that positive expression of RETNLB was detected in most tissues from gastric carcinoma and colon cancer patients, RETNLB was also found involvement in oral squamous cell carcinoma [PMID: 34158059 19706296 27001185 15983036].
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for RETNLB antibody 18232-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |