验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
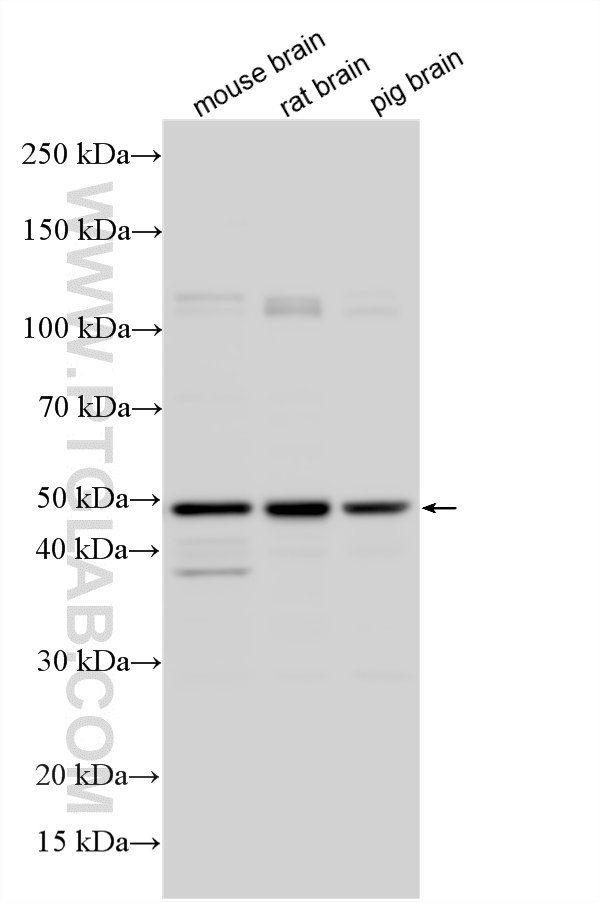
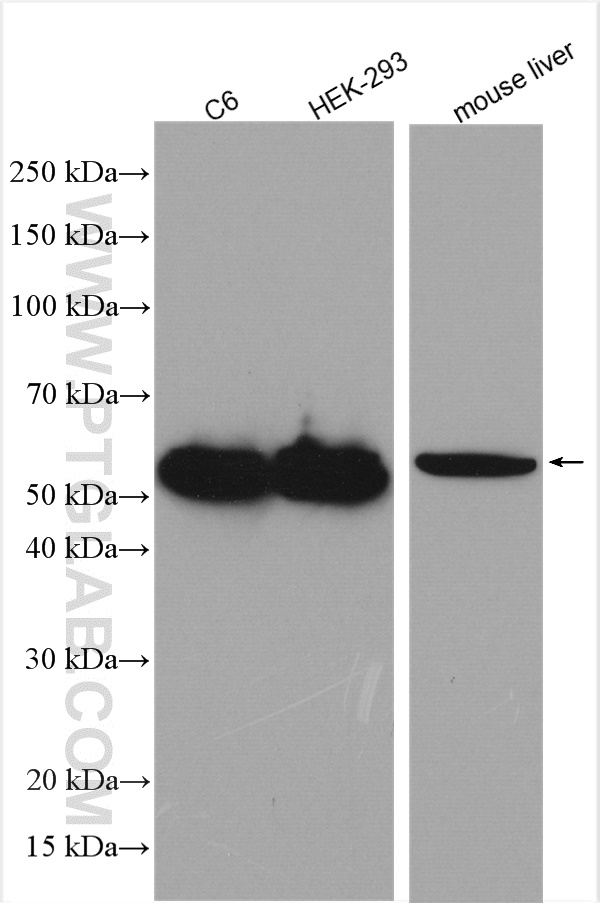
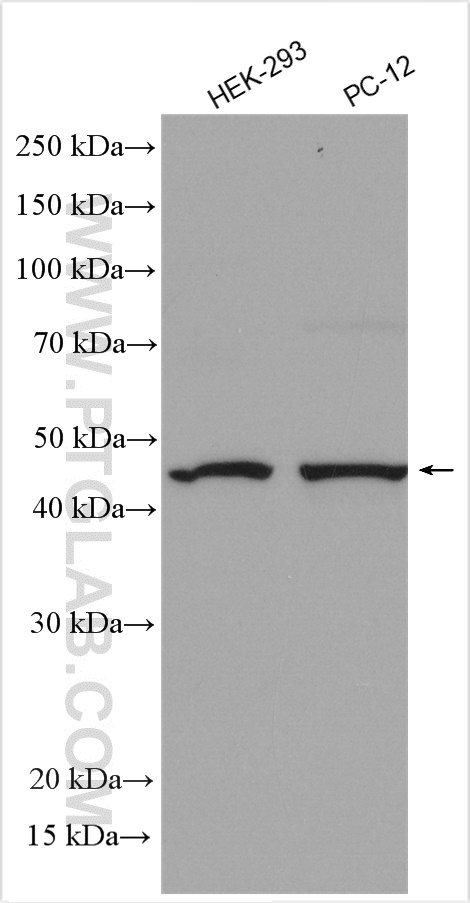
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, C6 cells, HEK-293 cells, mouse liver tissue, PC-12 cells, rat brain tissue, pig brain tissue |
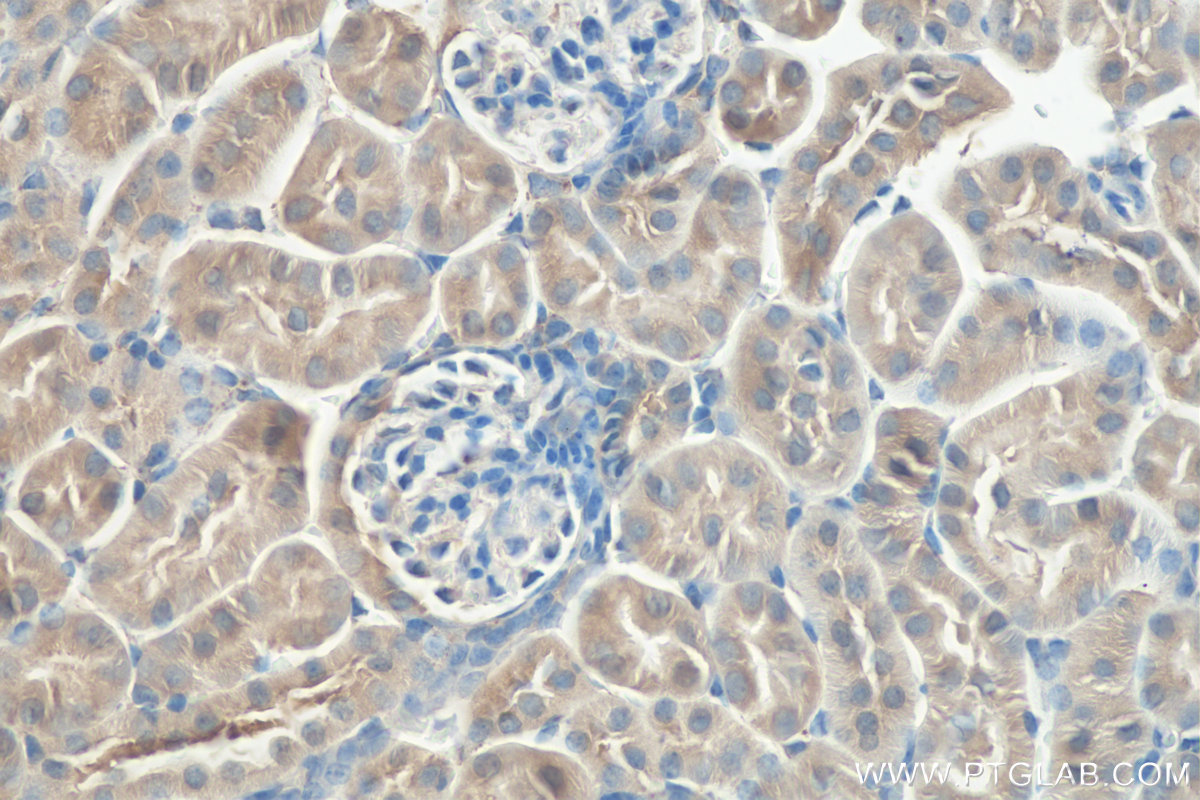
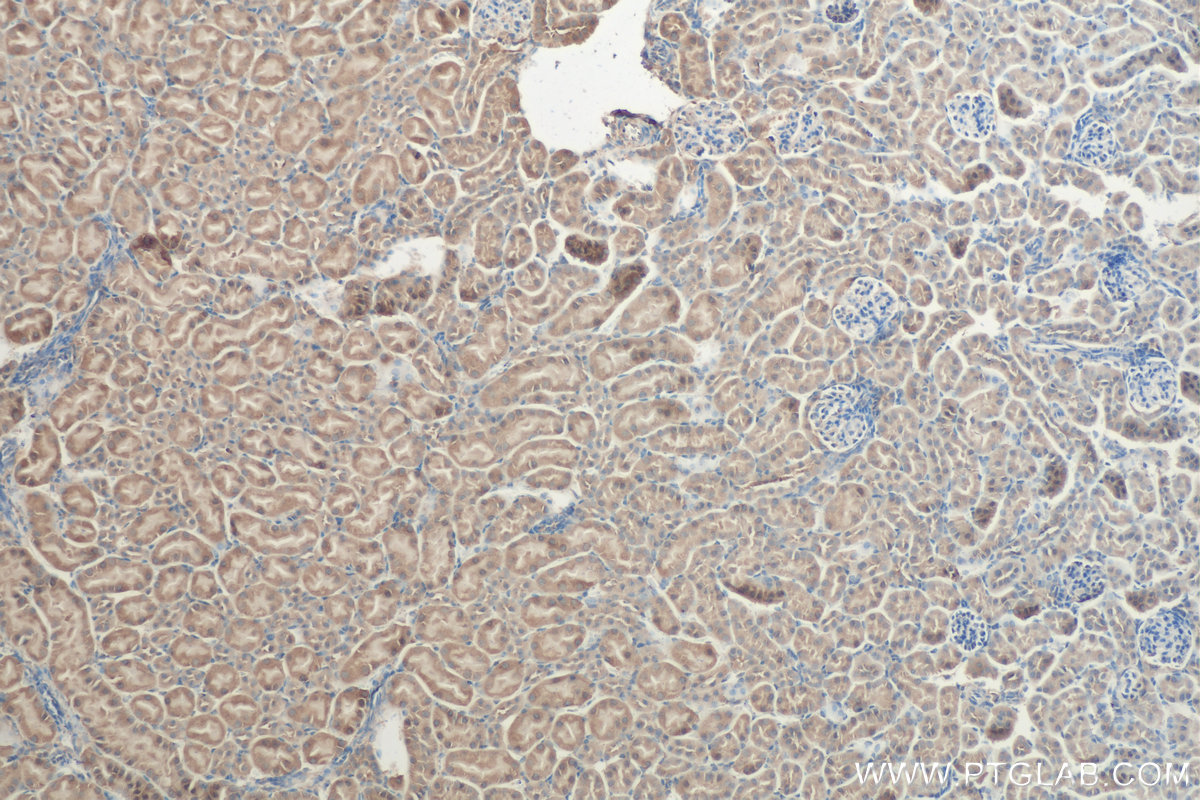
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
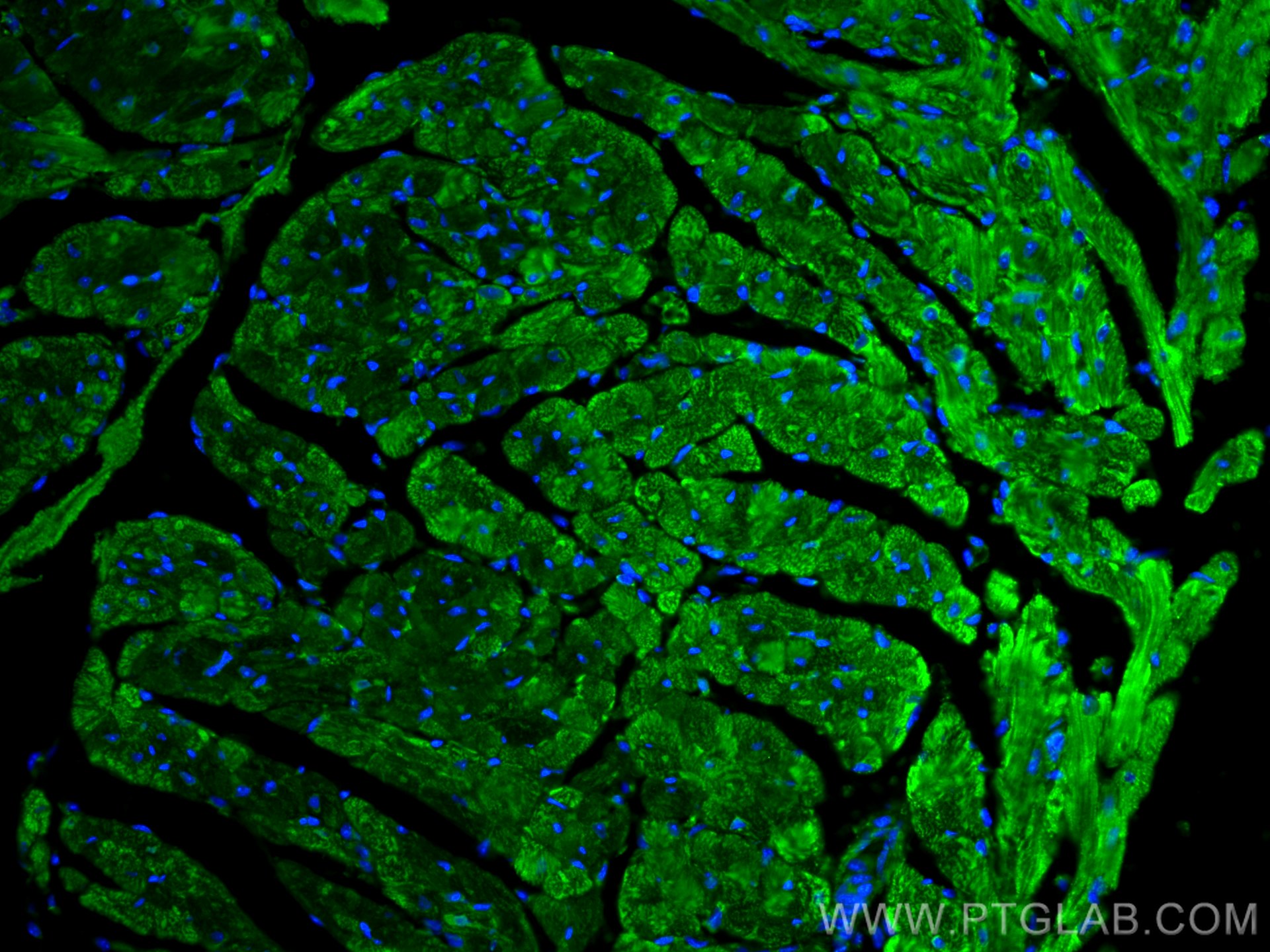
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse heart tissue, mouse brain tissue |
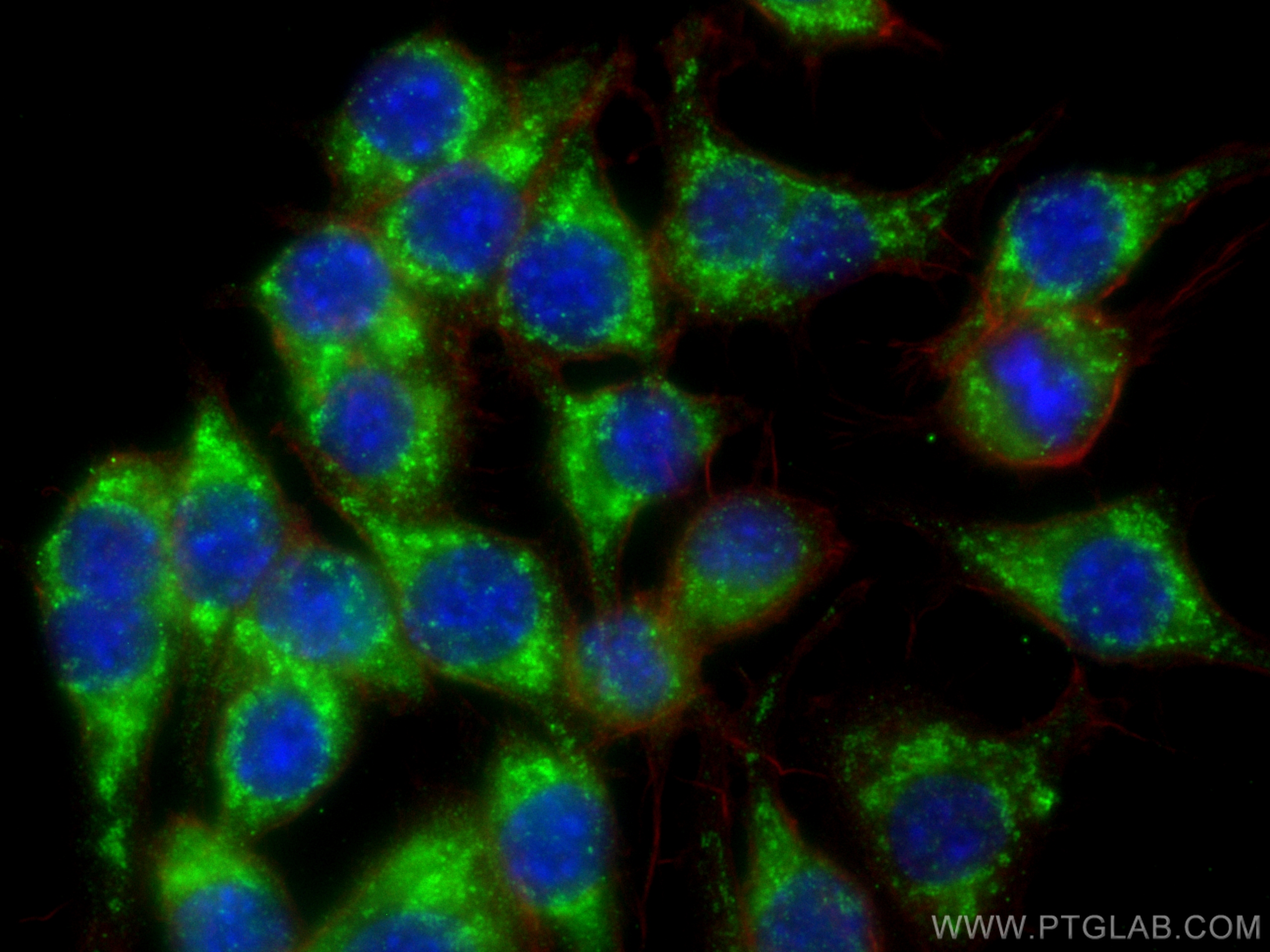
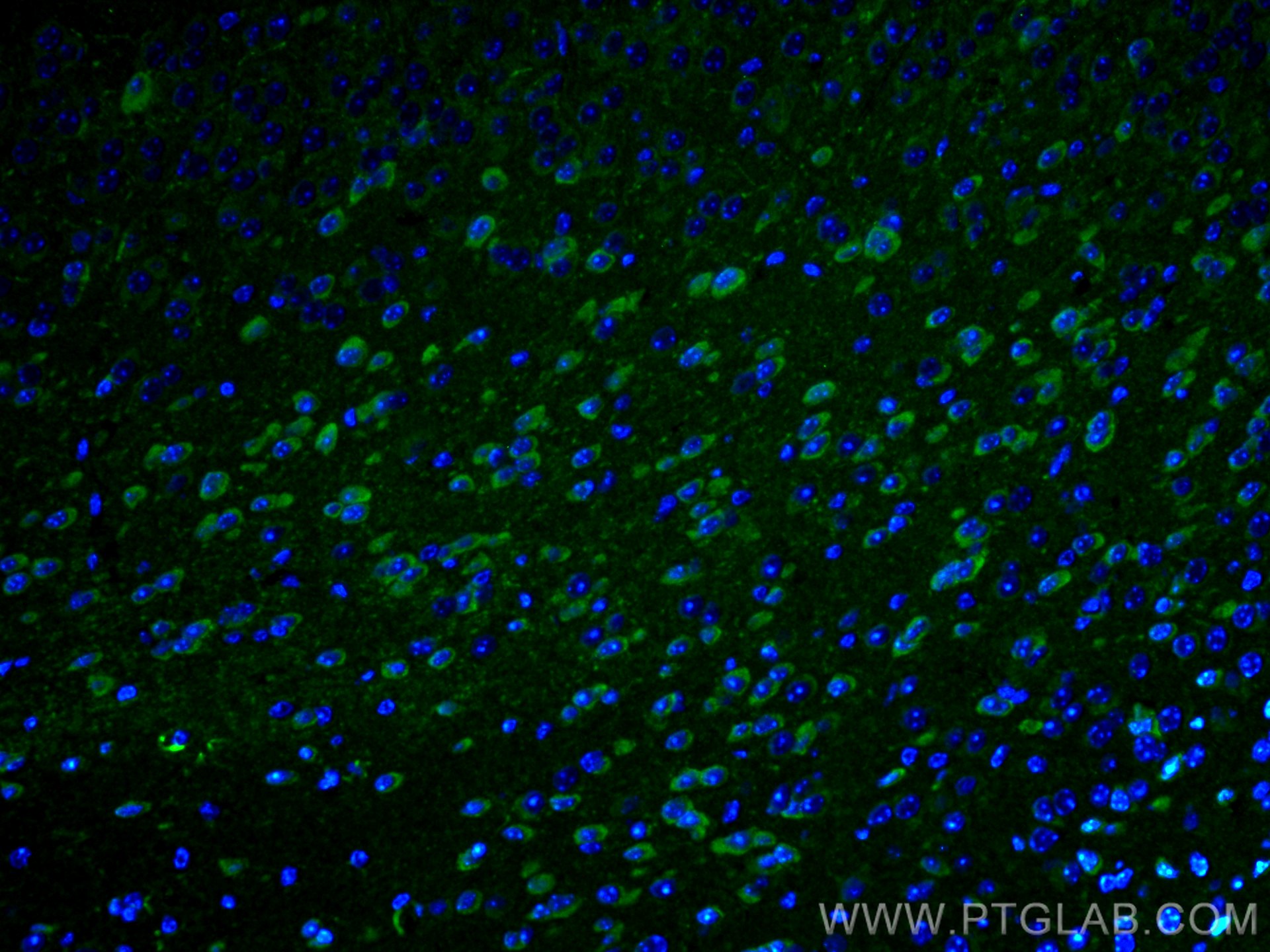
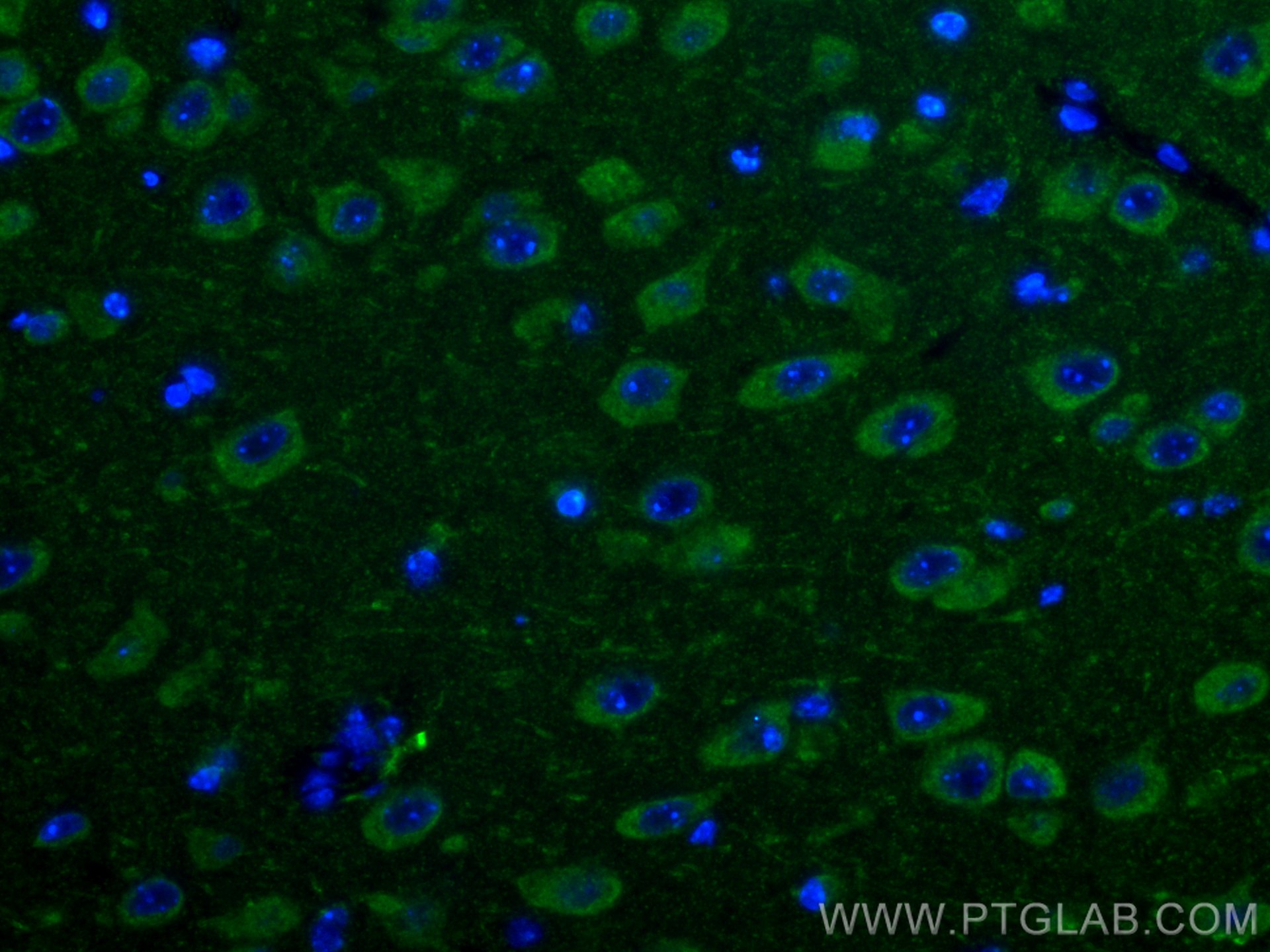
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | RAW 264.7 cells |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
14060-1-AP targets PARK2/Parkin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat, pig |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit, monkey, chicken, bovine, cattle, ducks |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag5092 Product name: Recombinant human Parkin protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 81-387 aa of BC022014 Sequence: NATGGDDPRNAAGGCEREPQSLTRVDLSSSVLPGDSVGLAVILHTDSRKDSPPAGSPAGRSIYNSFYVYCKGPCQRVQPGKLRVQCSTCRQATLTLTQGPSCWDDVLIPNRMSGECQSPHCPGTSAEFFFKCGAHPTSDKETSVALHLIATNSRNITCITCTDVRSPVLVFQCNSRHVICLDCFHLYCVTRLNDRQFVHDPQLGYSLPCVGTGDTVVLRGALGGFRRGVAGCPNSLIKELHHFRILGEEQYNRYQQYGAEECVLQMGGVLCPRPGCGAGLLPEPDQRKVTCEGGNGLGCGYGQRRTK 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | Parkinson disease (autosomal recessive, juvenile) 2, parkin |
| 别名 | PARK2, Parkin, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase parkin, EC:2.3.2.31, Parkin RBR E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase |
| 计算分子量 | 52 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 42-52 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC022014 |
| 基因名称 | Parkin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5071 |
| RRID | AB_2878005 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O60260 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Parkin, a RING-type E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase, is involved in the ubiquitination pathway and contributes to protection from neurotoxicity induced by unfolded protein stresses. Its ubiquitin-protein ligase activity promotes the degradation of a variety of proteins including itself. Mutations in Parkin are implicated in the pathogenesis of autosomal recessive familial Parkinson's disease. It has 8 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with molecular weights of 24, 31, 36 and 42-52 kDa. Sometimes an additional band of 70 kDa or 110 kDa may be detected, which is caused by ubiquitination modification or formation of Parkin complex (PMID: 10976934, PMID: 18190519).
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for PARK2/Parkin antibody 14060-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for PARK2/Parkin antibody 14060-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for PARK2/Parkin antibody 14060-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Cell Biol Ammonia-induced lysosomal and mitochondrial damage causes cell death of effector CD8+ T cells | ||
Nat Commun Augmented temperature fluctuation aggravates muscular atrophy through the gut microbiota | ||
Acta Pharm Sin B Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit cervical cancer growth through Parkin acetylation-mediated mitophagy. | ||
Acta Pharm Sin B Engineering cannabidiol synergistic carbon monoxide nanocomplexes to enhance cancer therapy via excessive autophagy | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Lyophilized apoptotic vesicles restore DNA damage and mitochondria dysfunction to ameliorate radiation enteritis |