Recombinant Mouse RAGE protein (His Tag)
种属
Mouse
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse RAGE protein Gly23-Ala340 (Accession# Q62151-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 11596 |
| 蛋白编号 | Q62151-1 |
| 预测分子量 | 34.8 kDa |
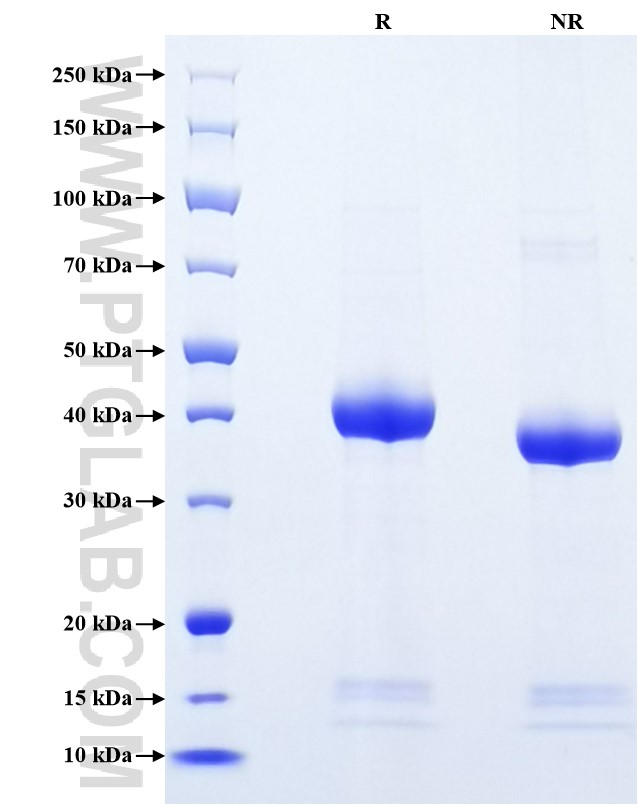
| SDS-PAGE | 37-45 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation endproducts), also called AGER, is a transmembrane receptor of the immunoglobulin super family. It mediates interactions of advanced glycosylation end products (AGE) which accumulate in vascular tissue in aging in diabetes. Acts as a mediator of vascular inflammation such as atherosclerosis and a complication of diabetes. AGE/RAGE signal regulates production or expression of TNF-alpha, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Interaction with S100A12 on endothelium, mononuclear phagocytes, and lymphocytes triggers cellular activation. Interaction with S100B after myocardial infarction regulates myocyte apoptosis by activating ERK1/2 and p53/TP53 signaling. ABPP-initiated RAGE signaling, especially stimulation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), delivers ABPP as a complex with RAGE to the intraneuronal. RAGE has higher expression in lung tissues, in particular in alveolar type I cells, and is lost in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
参考文献:
1. Neeper M. et al. (1992) J Biol Chem. 267(21):14998-5004. 2. Hofmann MA. et al. (1999) Cell. 97(7):889-901. 3. Markus A. et al. (2008) Am J Respir Cell Mol Bio. 39(3):337-45. 4. Xue G. et al. (2008) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295(2):H491-8. 5. Takuma K. et al. (2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106(47):20021-6. 6. Fang F. et al. (2010) FASEB J. 24(4):1043-55.