Recombinant Mouse NCAM-1/CD56 protein (His Tag)(HPLC verified)
种属
Mouse
纯度
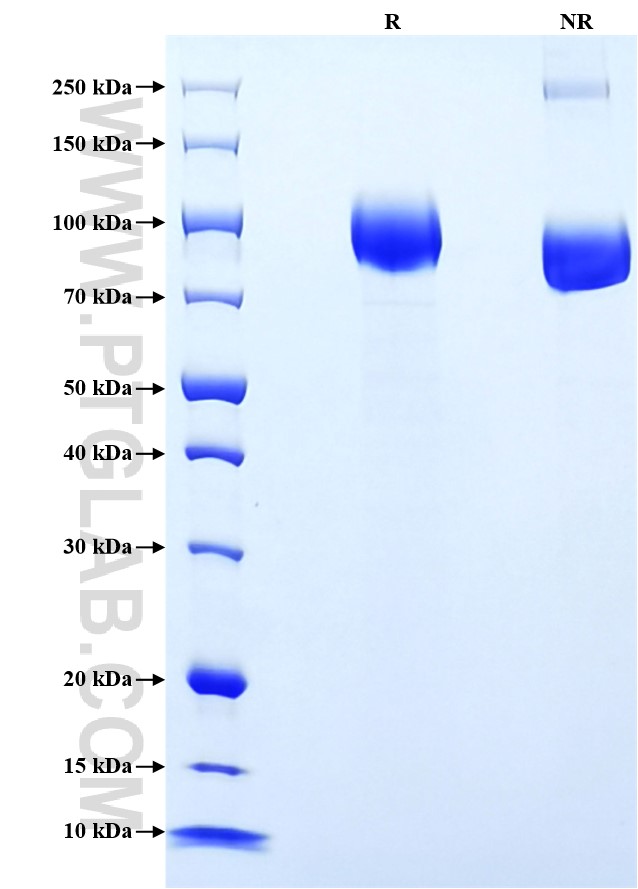
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
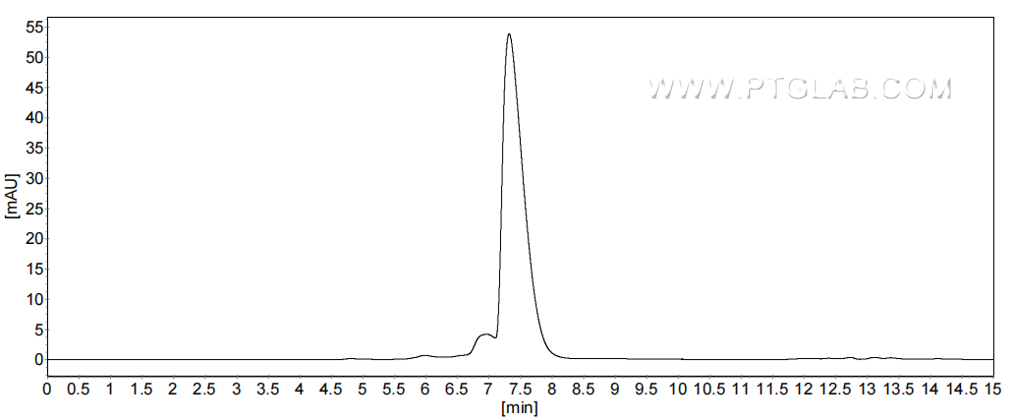
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse NCAM-1 protein Leu20-Thr711 (Accession# P13595-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 17967 |
| 蛋白编号 | P13595-1 |
| 预测分子量 | 80.5 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 80-110 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurons, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety of human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas. Three major isoforms of NCAM1, with molecular masses of 120, 140, and 180 kDa, are generated by alternative splicing of mRNA. The glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored NCAM120 and the transmembrane NCAM140 and NCAM180 consist of five Ig-like domains and two fibronection-type III repeats (FNIII). All three forms can be posttranslationally modified by addition of polysialic acid (PSA). Several other isofroms have also been described.
参考文献:
1. Maria-Isabel T.et al. (1998).J Virol.72(9):7181-7190. 2. Ralf K.et al. (2004). Nat Rev Neurosci.5(3):195-208. 3. E Phimister.et al. (1991).J Clin Pathol.44(7):580-585. 4. AdamN.et al. (2017). ImmunolLett.185:93-97. 5. Markus A.et al. (2019). Acta Neurol Scand.139(5):422-427.