Recombinant Mouse IL-6 protein (His Tag)
种属
Mouse
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
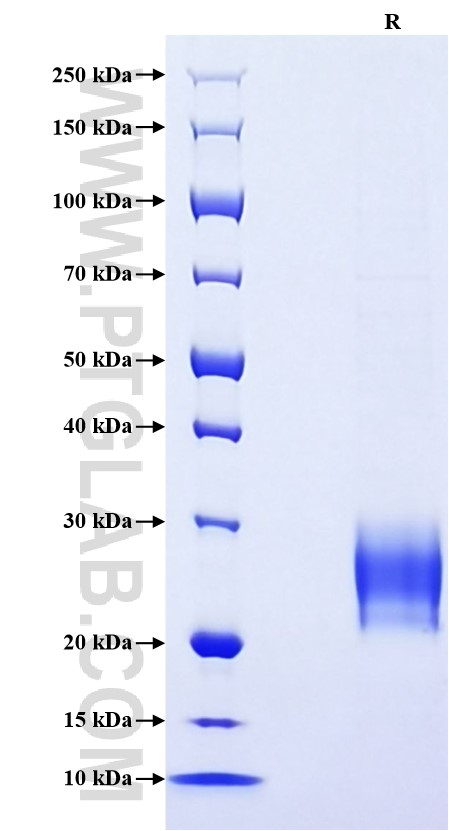
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse IL-6 protein Phe25-Thr211 (Accession# P08505) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 16193 |
| 蛋白编号 | P08505 |
| 预测分子量 | 22.8 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 22-30 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6 protein is secreted by a variety of cell types including T cells and macrophages as phosphorylated and variably glycosylated molecule. IL-6 plays an essential role in the final differentiation of B-cells into Ig-secreting cells involved in lymphocyte and monocyte differentiation. It induces myeloma and plasmacytoma growth and induces nerve cells differentiation. IL-6 is also considered a myokine, a cytokine produced from muscle, and is elevated in response to muscle contraction. IL-6 has been shown to interact with interleukin-6 receptor and glycoprotein 130. Additionally, IL-6 is involved in hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression, and has been defined an essential role in directing transition from innate to acquired immunity.
参考文献:
1. Heinrich, Peter C et al. The Biochemical journal vol. 374,Pt 1 (2003): 1-20. 2. Rose-John, Stefan et al. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets vol. 11,5 (2007): 613-24. 3. Ming, J E et al. The Journal of molecular and cellular immunology : JMCI vol. 4,4 (1989): 203-11; discussion 211-2.