Recombinant Mouse CXCL2 protein (rFc Tag) (HPLC verified)
种属
Mouse
纯度
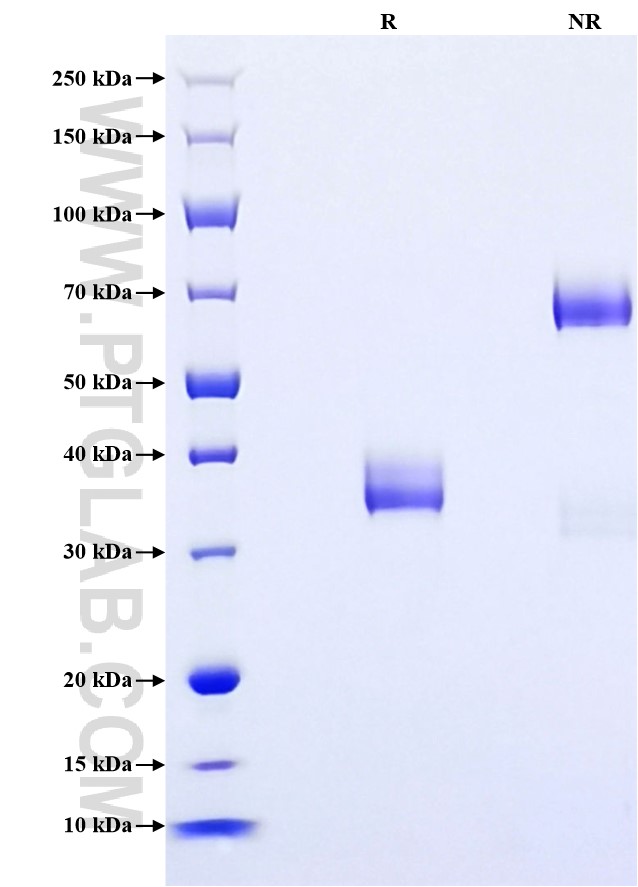
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
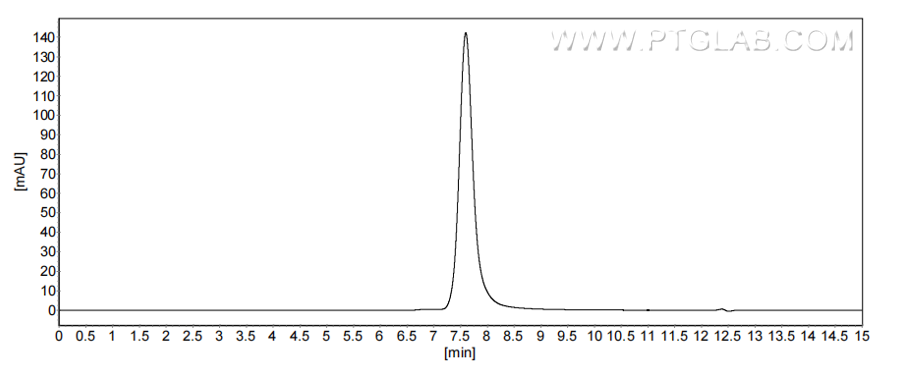
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
标签
rFc Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse CXCL2 protein Ala28-Asn100 (Accession# P10889) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the N-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 20310 |
| 蛋白编号 | P10889 |
| 预测分子量 | 35.0 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 34-38 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
CXCL2, also known as macrophage inflammatory protein 2-alpha (Mip2-alpha), is a member of CXC chemokine family that binds to CXC chemokine receptor 2 (CXCR2). CXCL2 is mainly produced by macrophages, endothelial cells, epithelial cells and tumor cells. CXCL2 plays important roles in various biological progresses such as angiogenesis, inflammation, immune response and cancer biological behaviors. Under inflammatory conditions in CNS, microglia and astrocytes may secrete CXCL2 as well as other chemokines, which induces chemotaxis and infiltration of circulatory neutrophils. Indeed, previous studies suggest that CXCL2 is involved in Alzheimer disease, multiple sclerosis and brain ischemia.
参考文献:
1. Vansaun MN. et al. (2013). PLoS One. 8(9):e73054. 2. Jablonska J. et al. (2014). Int J Cancer. 134:1346-58. 3. Oue E. et al. (2012). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 424:456-461. 4. Haraguchi K. et al. (2012). J. Neurosci.32:3931-3941. 5. L. Bozoyan. et al. (2015). J. Neuroinflammation. 12:173. 6. Hosking MP. et al. (2010). PLoS One. 5(6):e11340.