Recombinant Mouse Albumin protein (His Tag)
种属
Mouse
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Mouse Albumin protein Glu25-Ala608 (Accession# P07724) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 11657 |
| 蛋白编号 | P07724 |
| 预测分子量 | 67.0 kDa |
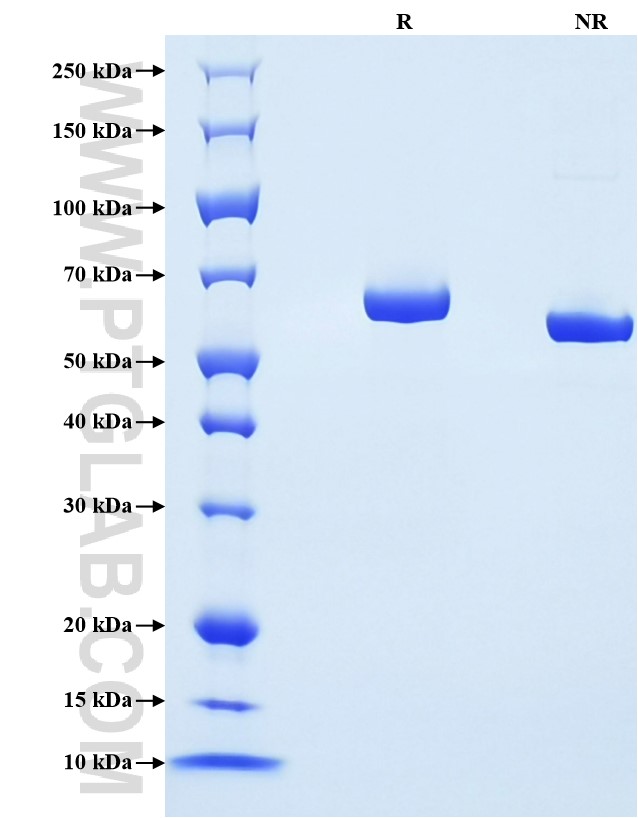
| SDS-PAGE | 60-68 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Albumin is one of the main proteins in animal species, which plays a decisive role in the transport of various ions and in maintaining the colloidal osmotic pressure of the blood. Albumin is able to bind to almost all known drugs, as well as many nutraceuticals and toxic substances, largely determining their pharmaco-and toxicokinetics. Albumin is not only passive, but also an active participant of pharmacokinetic and toxicokinetic processes, possessing a number of enzymatic activities. Numerous experiments have shown esterase or pseudoesterase activity of albumin towards a number of endogeneous and exogeneous esters. Due to the free thiol group of Cys34, albumin can serve as a trap for reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, thus participating in redox processes. Glycated albumin makes a significant contribution to the pathogenesis of diabetes and other diseases. The interaction of albumin with blood cells, blood vessels and tissue cells outside the vascular bed is of great importance. Interactions with endothelial glycocalyx and vascular endothelial cells largely determine the integrative role of albumin.
参考文献:
1. Belinskaia DA, et al. (2021). J Evol Biochem Physiol. 57(6):1419-1448. 2. Raoufinia R, et al. (2016). Adv Pharm Bull. 6(4):495-507. 3. Sleep D. (2015). Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 12(5):793-812. 4. Nakashima F, et al. (2018). Sci Rep. 17;8(1):932. 5. He XM, et al. (1992). Nature. 358(6383):209-15.