Recombinant Human Siglec-7/CD328 protein (His Tag)
种属
Human
纯度
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
标签
His Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human Siglec-7 protein Gln19-Leu353 (Accession# Q9Y286-1) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 27036 |
| 蛋白编号 | Q9Y286-1 |
| 预测分子量 | 38.0 kDa |
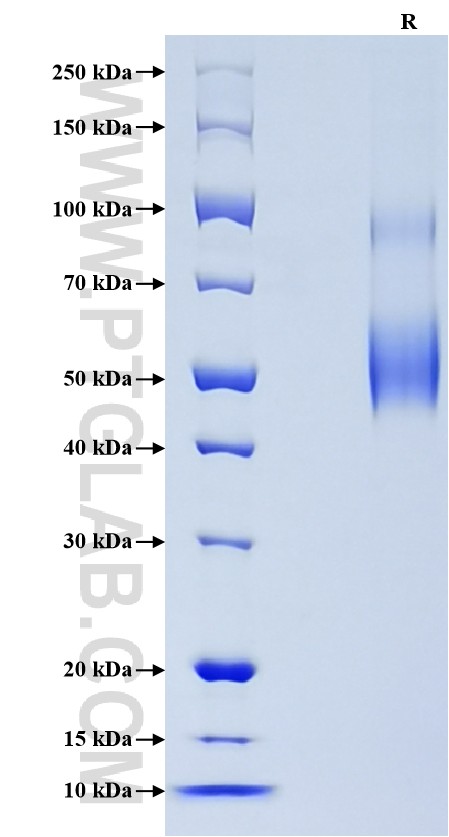
| SDS-PAGE | 45-65 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 7 (Siglec-7), also known as CD328 or p75/AIRM-1, is a member of the Siglec family of glycan-recognition proteins. Siglec-7 is a type-I transmembrane protein consisting of three extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains that comprise an N-terminal V-set domain and two C2-set domains, a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail containing two tyrosine residues embodied in immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motif-like motifs. It is mainly expressed on immune cells, with low levels on granulocytes, intermediate levels on monocytes, and relatively high levels on a major subset of natural killer cells and a minor subset of CD8+ T cells. Siglec-7 is an inhibitory receptor that negatively regulates the function of NK cells and modulates the immune response through the interaction of sialic acid-containing ligands .
参考文献:
1. Zheng, Yayun et al. Journal of immunology research vol. 2020 6243819. 2. Nicoll, G et al. The Journal of biological chemistry vol. 274,48 (1999): 34089-95. 3. Shao, J-Y et al. Scandinavian journal of immunology vol. 84,3 (2016): 182-90.