验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
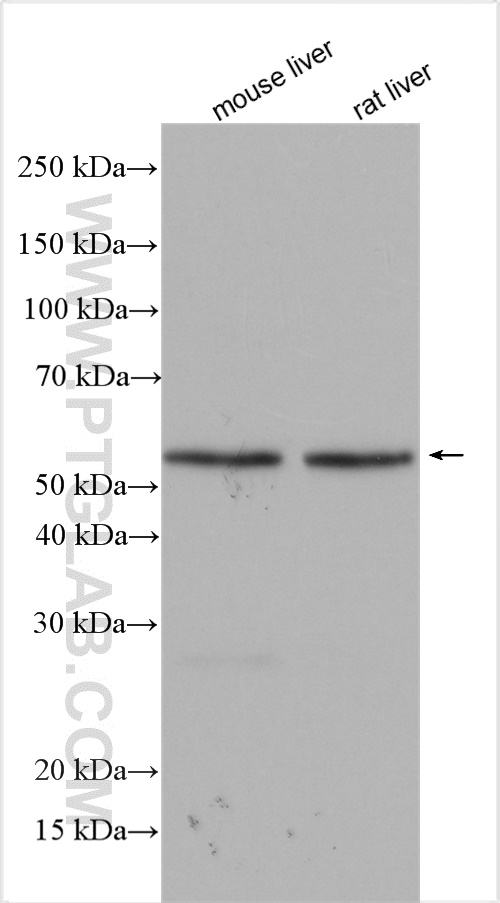
| Positive WB detected in | mouse liver tissue, rat liver tissue |
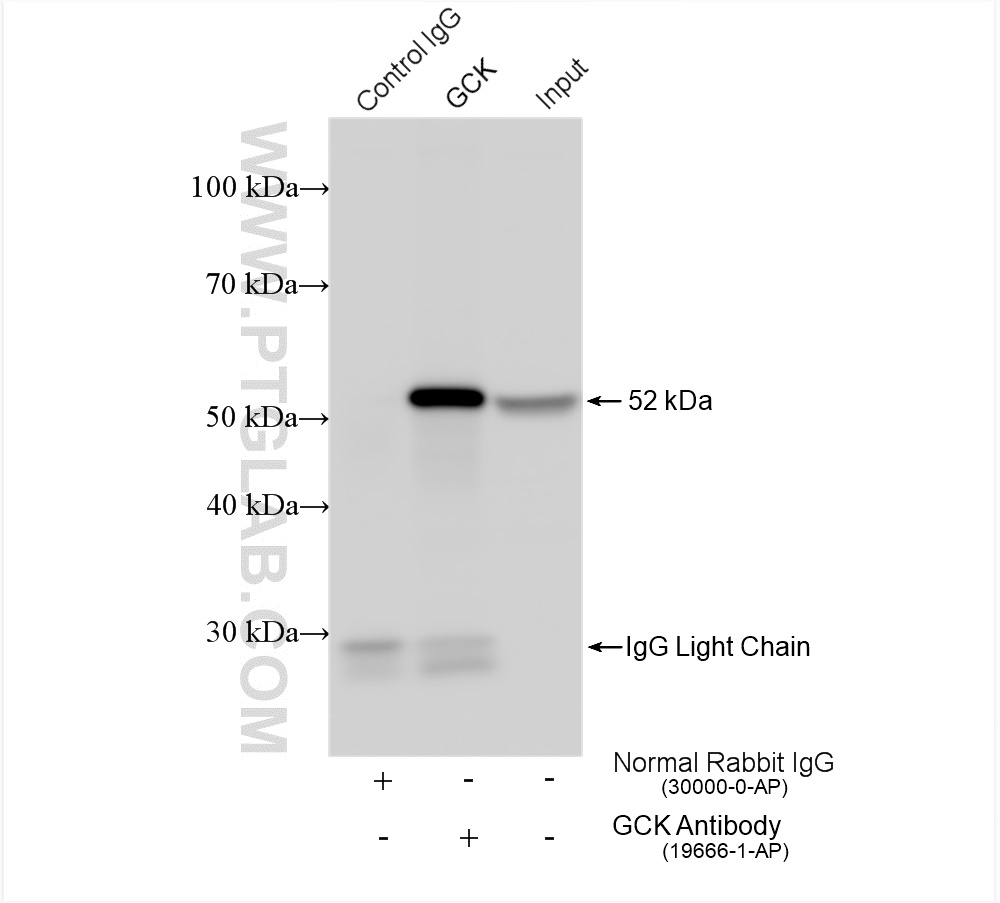
| Positive IP detected in | mouse liver tissue |
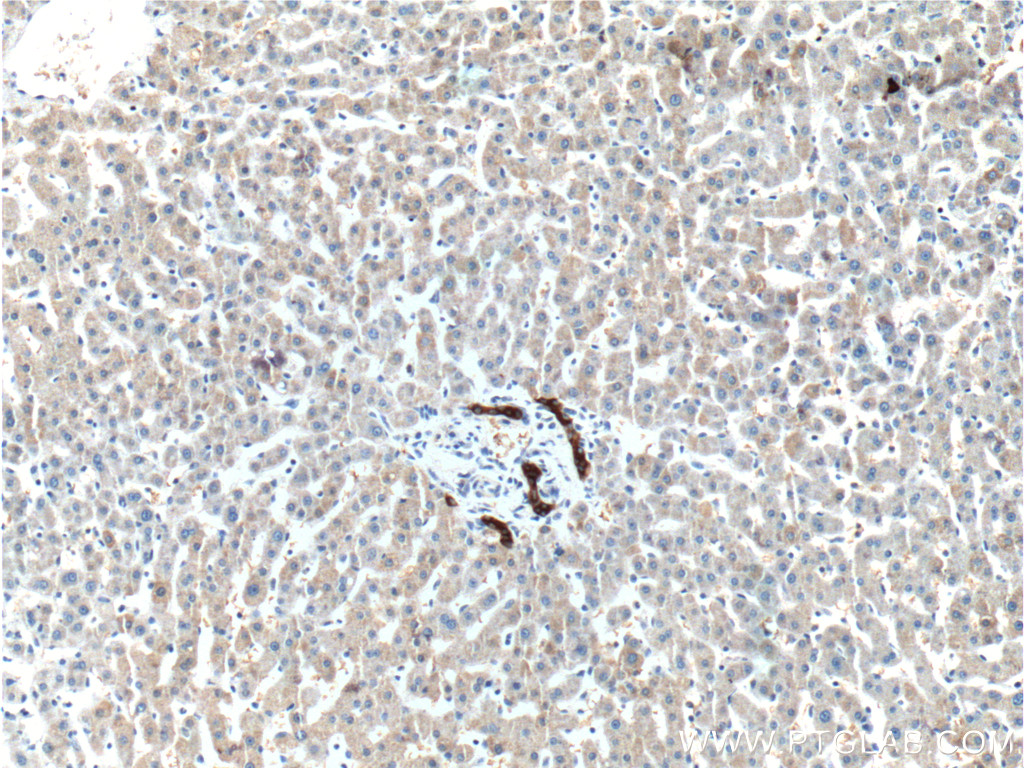
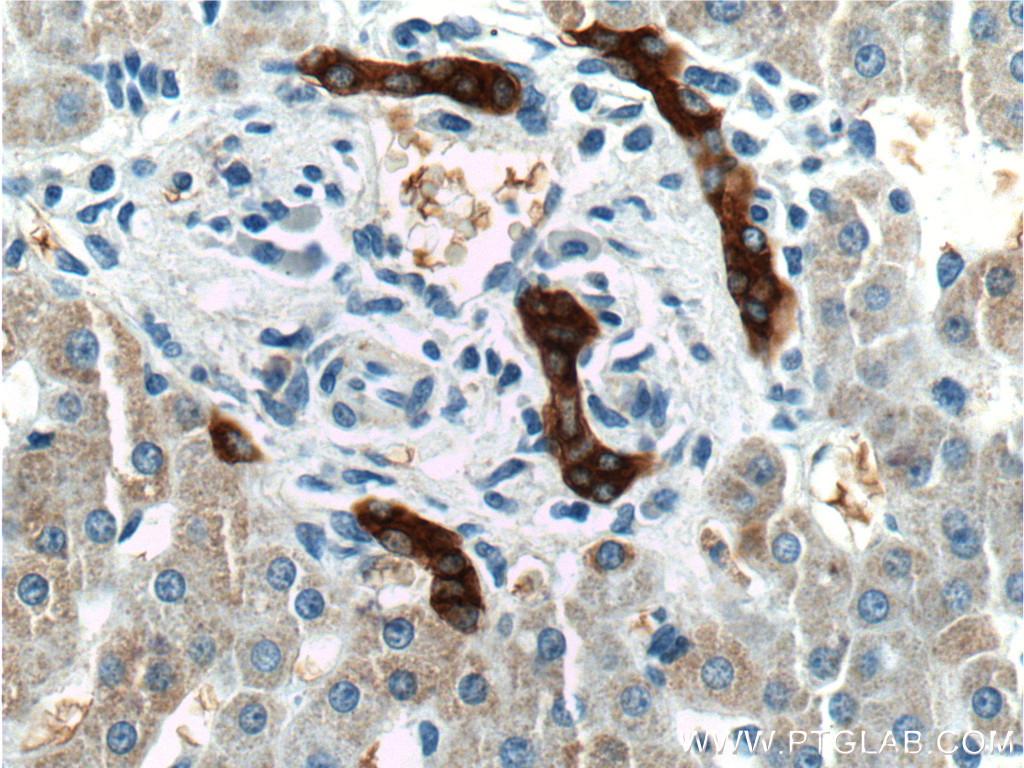
| Positive IHC detected in | human liver tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
This antibody is not recommended for WB detection of human samples.
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:100-1:400 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
19666-1-AP targets GCK in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, IP, ELISA Application Description |
| 文献引用应用 | WB, IHC, IF |
| 经测试反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 文献引用反应性 | human, mouse, rat |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag8116 Product name: Recombinant human GCK protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 157-465 aa of BC001890 Sequence: EDIDKGILLNWTKGFKASGAEGNNVVGLLRDAIKRRGDFEMDVVAMVNDTVATMISCYYEDHQCEVGMIVGTGCNACYMEEMQNVELVEGDEGRMCVNTEWGAFGDSGELDEFLLEYDRLVDESSANPGQQLYEKLIGGKYMGELVRLVLLRLVDENLLFHGEASEQLRTRGAFETRFVSQVESDTGDRKQIYNILSTLGLRPSTTDCDIVRRACESVSTRAAHMCSAGLAGVINRMRESRSEDVMRITVGVDGSVYKLHPSFKERFHASVRRLTPSCEITFIESEEGSGRGAALVSAVACKKACMLGQ 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | glucokinase (hexokinase 4) |
| 别名 | EC:2.7.1.1, Glucokinase, Hexokinase-4, Hexokinase-D, HK IV |
| 计算分子量 | 52 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 52 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC001890 |
| 基因名称 | GCK |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2645 |
| RRID | AB_10863656 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35557 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
背景介绍
Glucokinase (GCK) is a structurally and functionally unique member of hexokinase family. It is expressed only in mammalian liver and pancreatic islet beta cells. Because of its unique functional characteristics, the enzyme plays an important regulatory role in glucose metabolism.The rate of glucose metabolism in liver and pancreas is a function of the activity of the enzyme(PMID:1740341). Moreover, GCK has been found to have relationship with diabetes. Defects in GCK are the cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 2 (MODY2) and familial hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia type 3 (HHF3). It has 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the same molecular mass of 52 kDa.
实验方案
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for GCK antibody 19666-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for GCK antibody 19666-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for GCK antibody 19666-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
发表文章
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Transl Med Cyb5r3-based mechanism and reversal of secondary failure to sulfonylurea in diabetes
| ||
Phytomedicine Gentiopicroside ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism in T2DM via targeting FGFR1 | ||
PLoS Biol Loss of hepatic aldolase B activates Akt and promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by destabilizing the Aldob/Akt/PP2A protein complex. | ||
iScience Mof plays distinct roles in hepatic lipid metabolism under healthy or non-alcoholic fatty liver conditions |