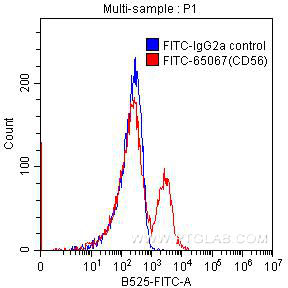
验证数据展示
经过测试的应用
| Positive FC detected in | Human peripheral blood lymphocytes |
推荐稀释比
| 应用 | 推荐稀释比 |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.2 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is 10 µl per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or 10 µl per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
产品信息
FITC-65067 targets NCAM1/CD56 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | FC Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
Acute myelogenous leukemia cell line KG-1 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Mouse / IgG2a, kappa |
| 抗体类别 | Monoclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| 别名 | CD56, NCAM1, NCAM 1, NCAM, N CAM 1 |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC014205 |
| 基因名称 | NCAM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4684 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000149294 |
| RRID | AB_2883757 |
| 偶联类型 | FITC Fluorescent Dye |
| 最大激发/发射波长 | 498 nm / 526 nm |
| 激发激光 | Blue laser (488 nm) |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P13591 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
背景介绍
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurones, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas.