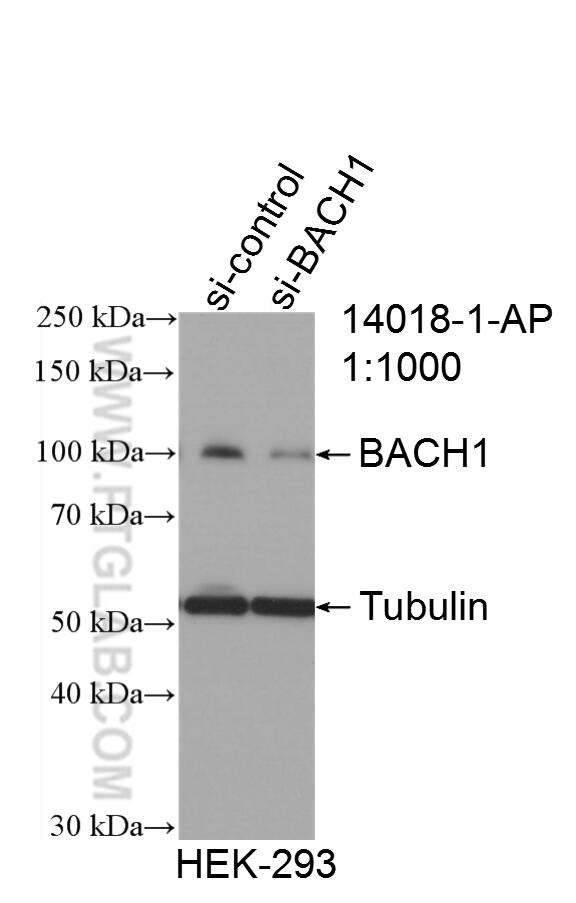
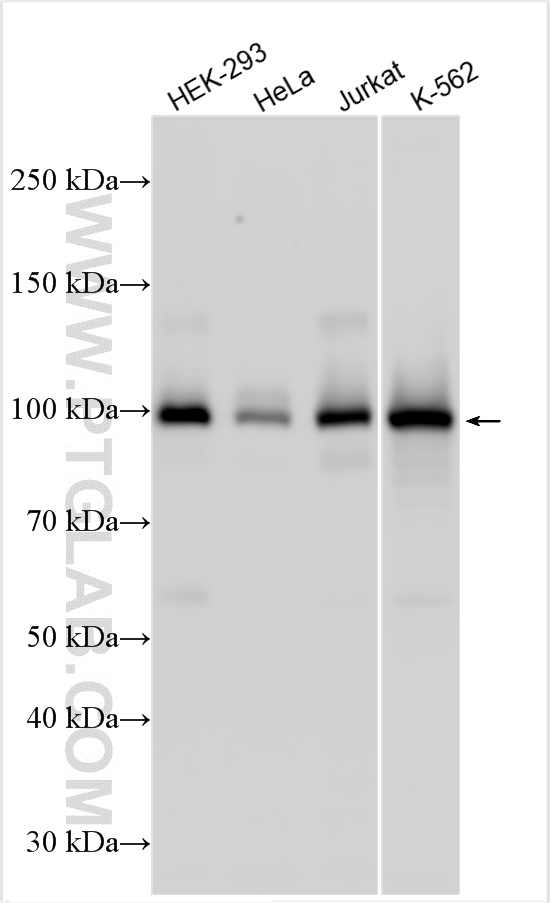
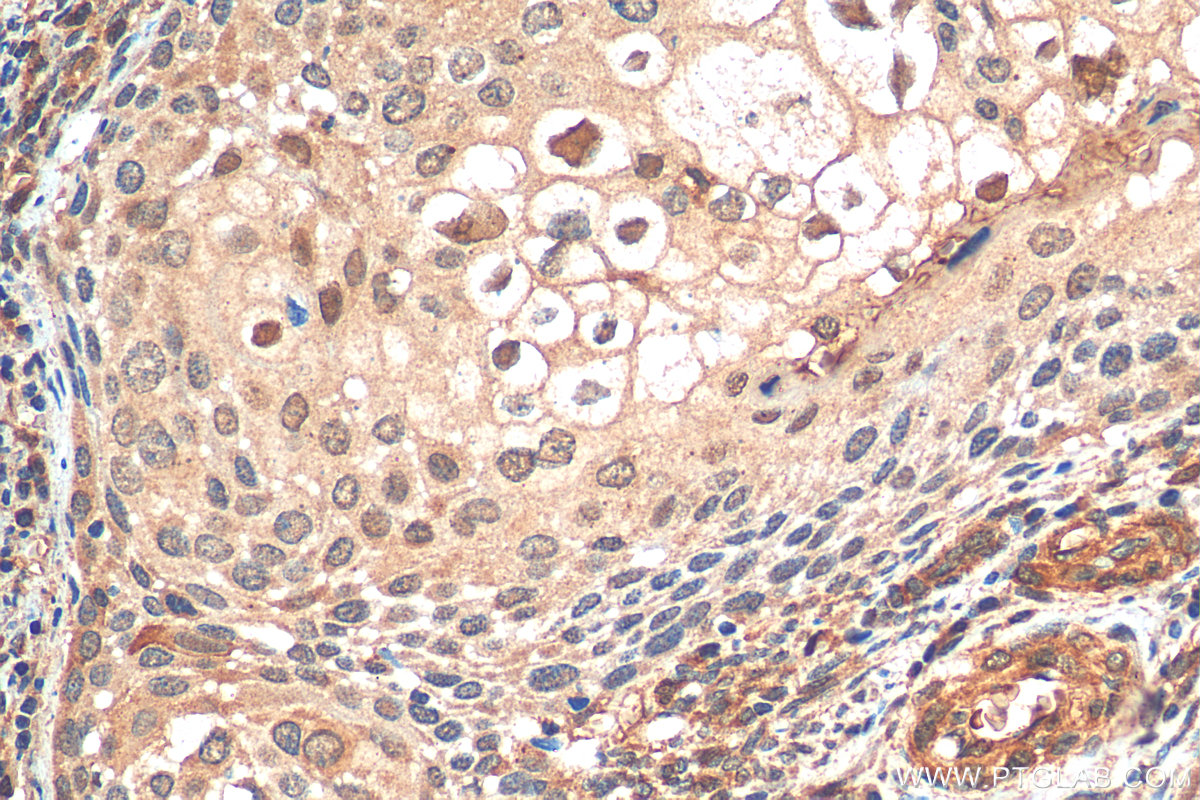
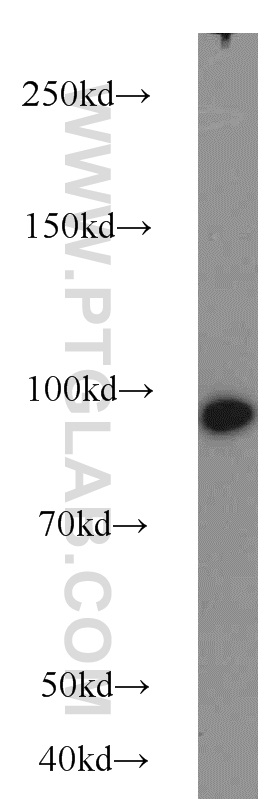
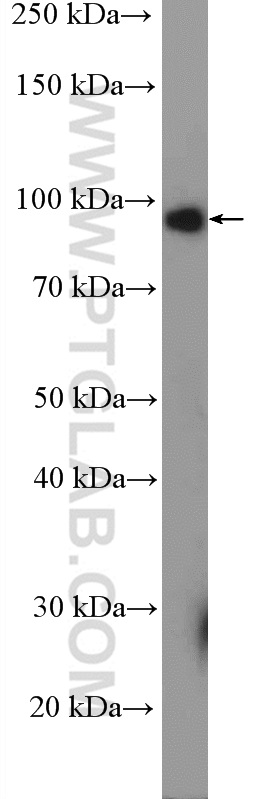
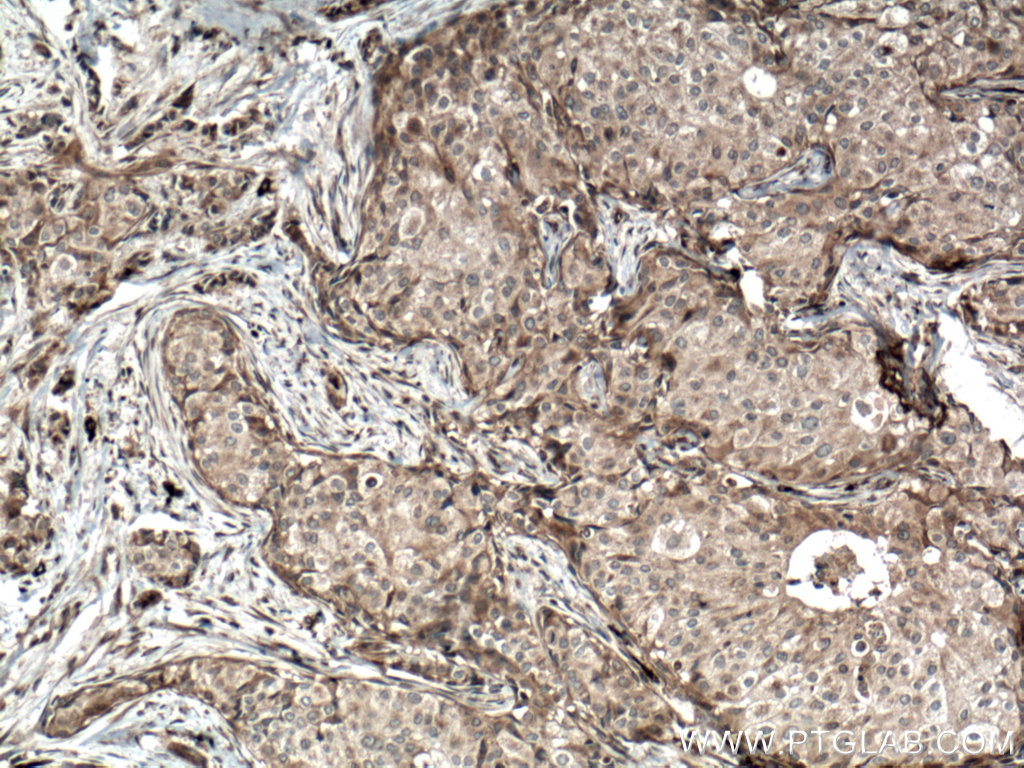
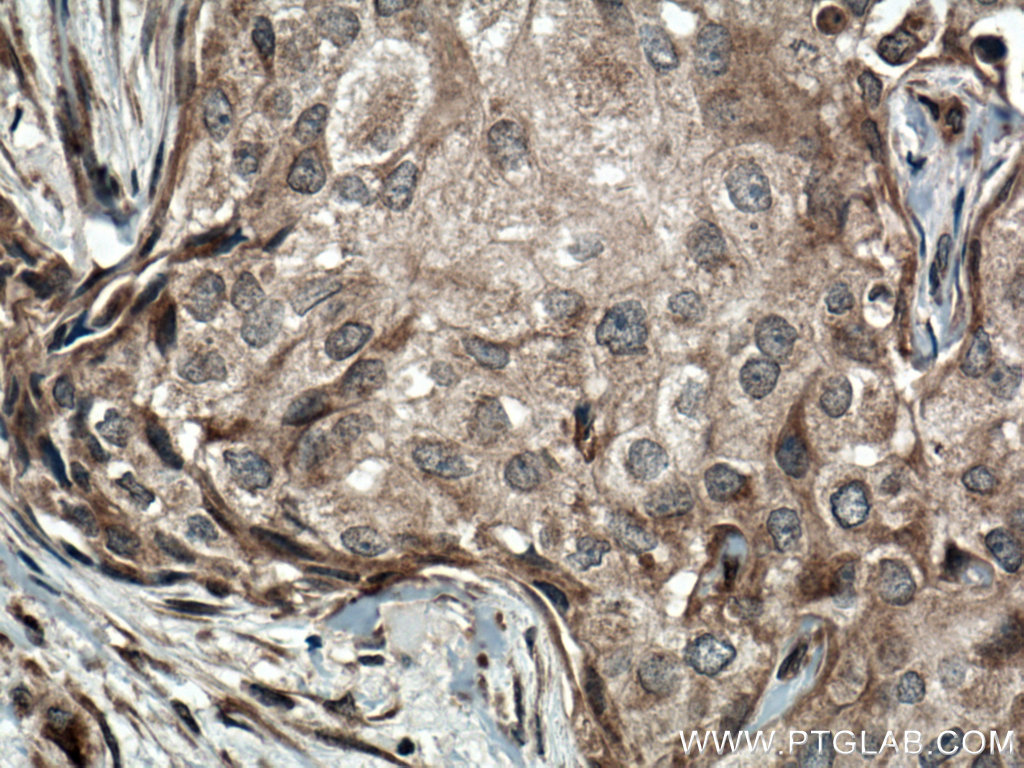
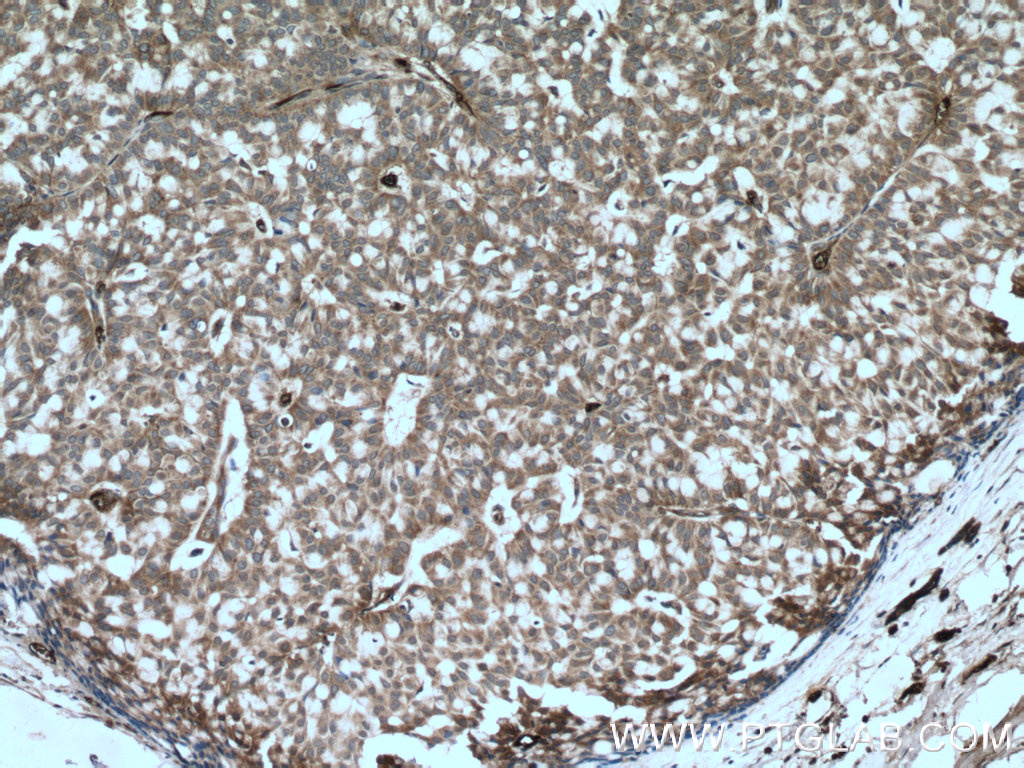
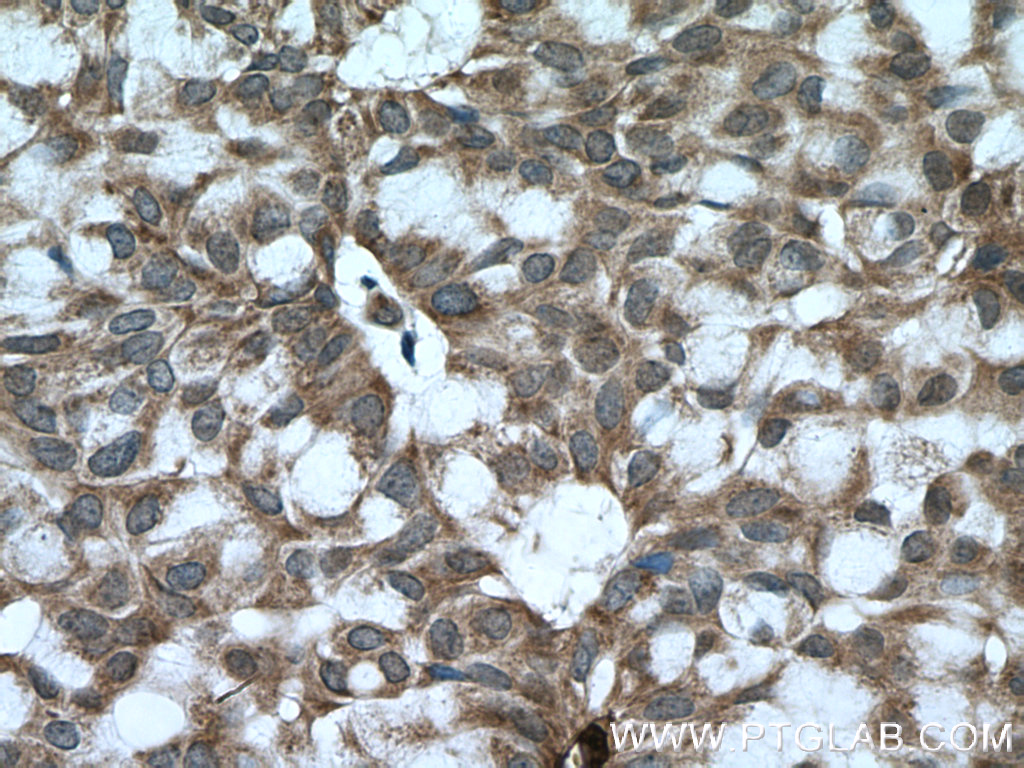
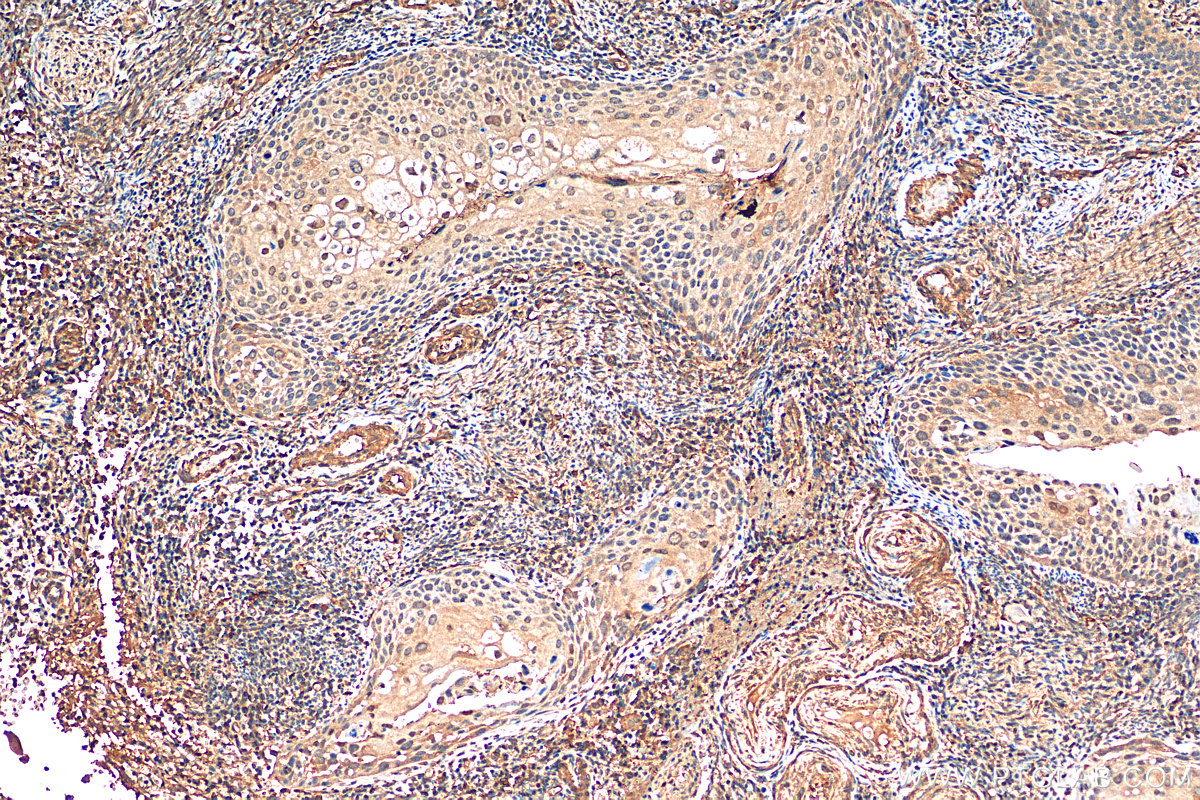
验证数据展示
产品信息
14018-1-PBS targets BACH1 in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| 经测试应用 | WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA Application Description |
| 经测试反应性 | human |
| 免疫原 |
CatNo: Ag5128 Product name: Recombinant human BACH1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 387-736 aa of BC063307 Sequence: SSVEREVAEHLAKGFWSDICSTDTPCQMQLSPAVAKDGSEQISQKRSECPWLGIRISESPEPGQRTFTTLSSVNCPFISTLSTEGCSSNLEIGNDDYVSEPQQEPCPYACVISLGDDSETDTEGDSESCSAREQECEVKLPFNAQRIISLSRNDFQSLLKMHKLTPEQLDCIHDIRRRSKNRIAAQRCRKRKLDCIQNLESEIEKLQSEKESLLKERDHILSTLGETKQNLTGLCQKVCKEAALSQEQIQILAKYSAADCPLSFLISEKDKSTPDGELALPSIFSLSDRPPAVLPPCARGNSEPGYARGQESQQMSTATSEQAGPAEQCRQSGGISDFCQQMTDKCTTDE 种属同源性预测 |
| 宿主/亚型 | Rabbit / IgG |
| 抗体类别 | Polyclonal |
| 产品类型 | Antibody |
| 全称 | BTB and CNC homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 |
| 别名 | BACH 1, BACH-1 |
| 计算分子量 | 82 kDa |
| 观测分子量 | 100-110 kDa |
| GenBank蛋白编号 | BC063307 |
| 基因名称 | BACH1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 571 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000156273 |
| RRID | AB_2274498 |
| 偶联类型 | Unconjugated |
| 形式 | Liquid |
| 纯化方式 | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14867 |
| 储存缓冲液 | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| 储存条件 | Store at -80°C. The product is shipped with ice packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at -80°C |
背景介绍
BTB and CNC homology 1 (Bach1) is a transcription factor expressed in many tissues, with key roles in cell cycle
regulation in homeostasis and in cancer in disease.
What is the molecular weight of BACH1?
Bach1 consists of 736 amino acids and is a member of the cap'n'collar type of basic region leucine zipper factor
family (CNC-bZip) with several atypical protein domains. Although its predicted MW is 82 kDa, it runs
anomalously at 100-110 kDa in SDS-PAGE.
What is the cellular localization of BACH1?
As it is a transcription factor, BACH1 is found in the nucleus of a number of mammalian cells, where it forms a
heterodimer with small Maf proteins. Once it has formed part of a heterodimer, BACH1 is able to bind to the
Maf recognition elements (MAREs) of target genes. During oxidative stress, BACH1 can be inactivated either by
heme or by cadmium, at which point it is exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it localizes to
microtubules (PMID: 15809329).
What is the function of BACH1?
BACH1 regulates the production of reactive oxygen species, with many of its downstream targets such as heme
oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NADPH quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) (PMID: 12356737; PMID: 15734732) involved
in the oxidative stress response. When the cell undergoes oxidative stress, BACH1 is displaced by nuclear factor
(erythroid-derived2)-like-2 (Nrf2), as both compete in binding to the MAREs in target genes. BACH1 also plays a
role in cell proliferation and survival, as it regulates several cell cycle genes such as cyclin-dependent kinase 6
(CDK6) and BCL2-like 11 (BCL2L11).
What is the role of BACH1 in disease?
BACH1 has been described in a number of cancer types, including breast, prostate, and melanoma. The function
of BACH1 appears varied in these tissues, with evidence that it may both promote and repress metastasis,
influence epigenetics, and regulate the growth of cancer cells (PMID: 22875853; PMID: 28889753; PMID: 26787
892). BACH1 may act on the same gene in different contexts to repress or activate it (PMID: 8887638).