AbFlex Histone H2A.XS139ph antibody (rAb)
Host / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Reactivity
Wide Range Predicted
Applications
WB
Cat No : 91395,91396 91395
Synonyms
验证数据展示
产品信息
| Tested Applications |
WB
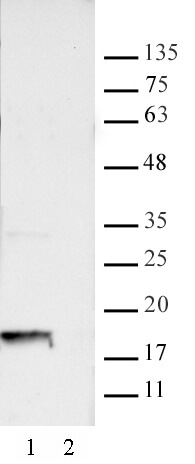
Validated Applications: WB:0.5 – 2 ug/ml *Note: cell lysates prepared by acid extraction is recommended for western blot. Please refer to the method outlines in Active Motif Histone Extraction Kit Manual, Cat. No. 40028, section B, for the protocol we use to prepare acid extracts from cells. |
| Tested Reactivity | Wide Range Predicted |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | This antibody was raised against a phospho-peptide corresponding to phospho-Histone H2AX (Ser139). |
| Full Name | AbFlex Histone H2A.XS139ph antibody (rAb) |
| Synonyms | Histone H2AX, H2A histone family member X, H2AX P-S139, antibody, antibodies,AbFlex, H2AXS139Ph, 39117 |
| Molecular weight | 15 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NP_002096 | Purification Method | Protein A Chromatography |
| Buffer | 140 mM Hepes, pH 7.5, 70 mM NaCl, 32 mM NaOAc, 0.035% sodium azide, and 30% glycerol. |
| Storage | Some products may be shipped at room temperature. This will not affect their stability or performance. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting items into single-use fractions for storage at -20°C for up to 2 years. Keep all reagents on ice when not in storage. |
背景介绍
Histone H2AX phospho Ser139 (H2AX, H2A histone family member X) replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries that require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called the histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Histone H2AX is required for checkpoint-mediated arrest of cell cycle progression in response to low doses of ionizing radiation, and for efficient repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), specifically when modified by C-terminal phosphorylation