Recombinant Human PTH protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
种属
Human
纯度
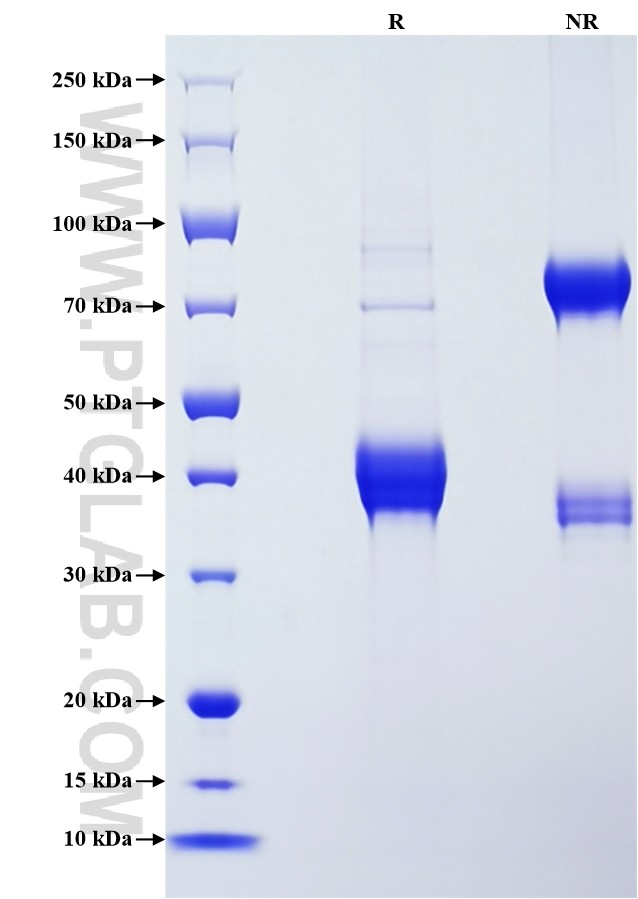
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
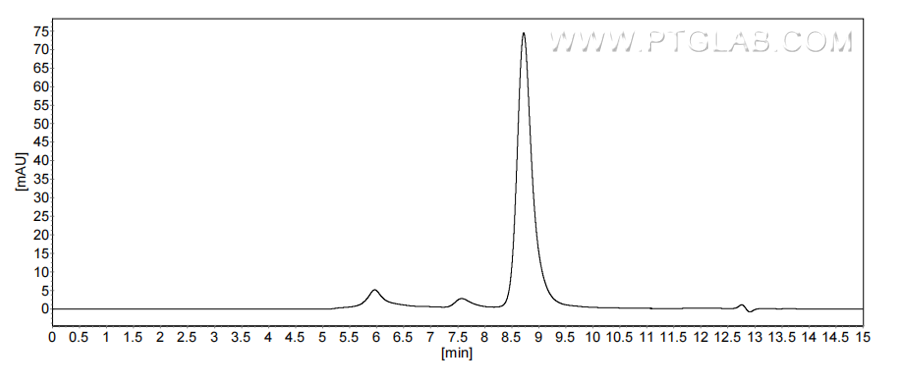
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
标签
rFc Tag
生物活性
未测试
验证数据展示
产品信息
| 纯度 | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| 内毒素 | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| 生物活性 |
Not tested |
| 来源 | HEK293-derived Human PTH protein Ser32-Gln115 (Accession# P01270) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| 基因ID | 5741 |
| 蛋白编号 | P01270 |
| 预测分子量 | 35.7 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 37-46 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| 组分 | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| 复溶 | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| 储存条件 |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| 运输条件 | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
背景信息
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also known as parathormone or parathyrin, is a critical peptide hormone that plays a vital role in calcium homeostasis within the human body. Secreted by the parathyroid glands, which are typically located behind the thyroid gland in the anterior neck, PTH is composed of 84 amino acids and is essential for maintaining serum calcium levels. The regulation of calcium is crucial not only for bone health but also for various physiological processes including muscle contraction, nerve function, and blood coagulation.Excessive secretion of PTH, often leading to hypercalcemia (elevated calcium levels) and associated symptoms such as kidney stones, osteoporosis, and neuropsychiatric disturbances. Conversely, insufficient PTH secretion can lead to hypocalcemia (low calcium levels), which may cause muscle cramps, spasms, and convulsions.
参考文献:
1.Dawale K,Agrawal A. (2022). Cureus. 14 (10):e30251. 2.Tang PK, et al. (2021)Vet J. 275:105719. 3.Jugade SC,Bhalchim S,Karkhanis A. (2022). Contemp Clin Dent. 13 (4):395-398.