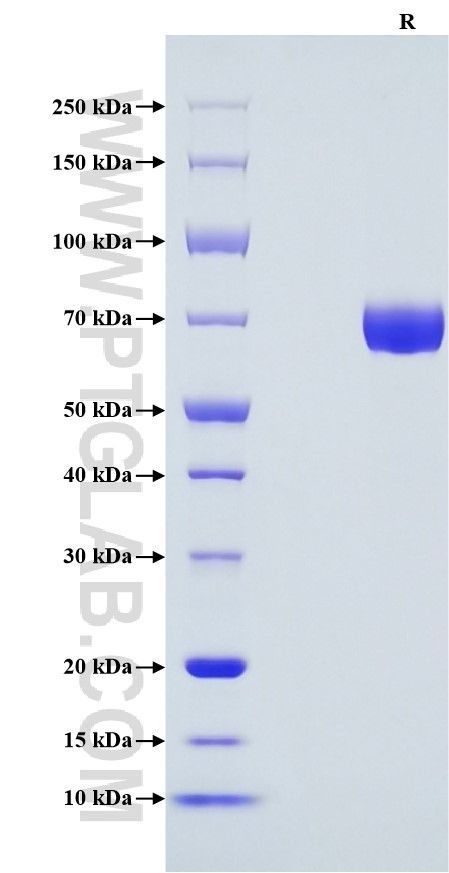
Recombinant Human IL-12 protein (His Tag)
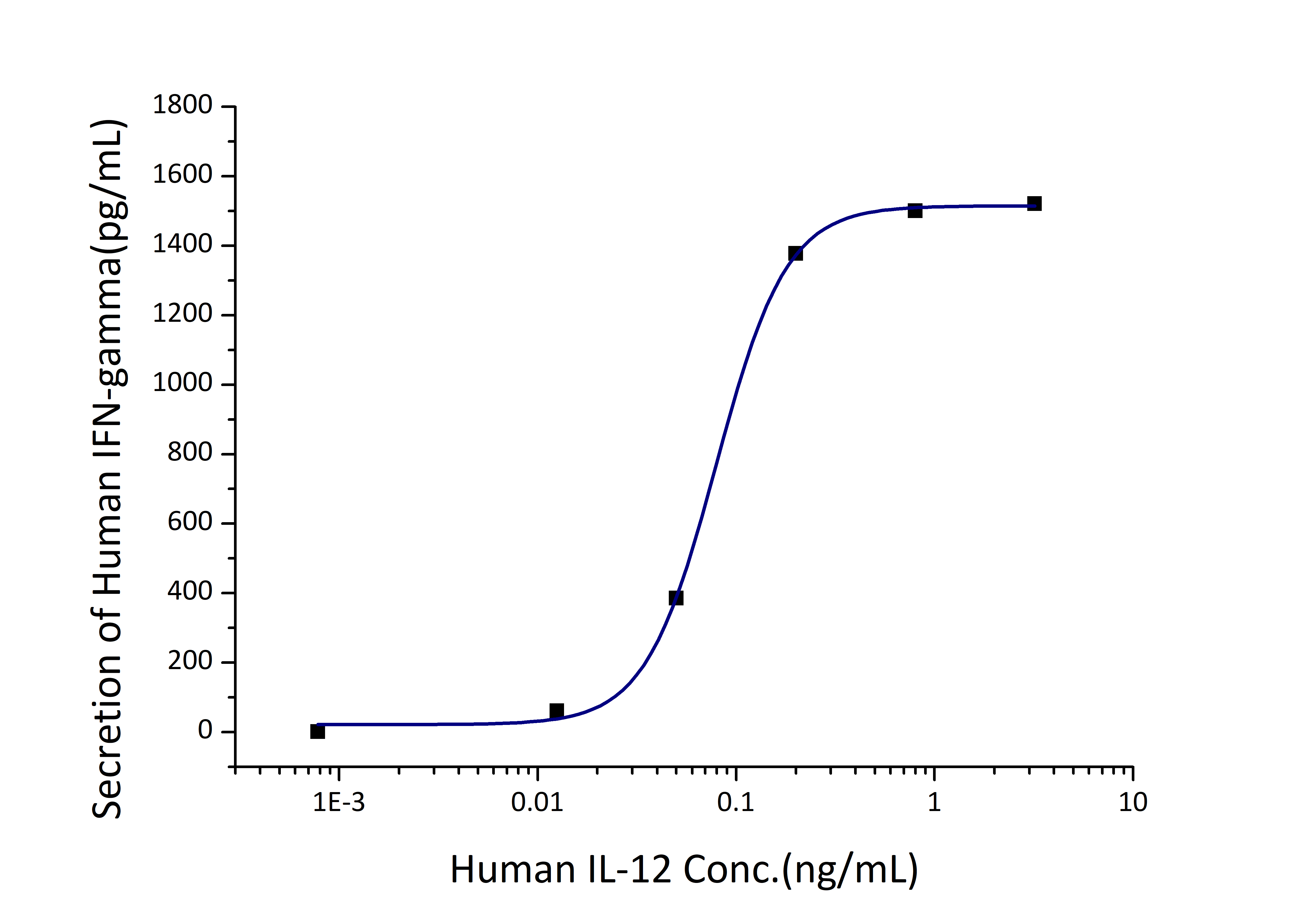
ED50
0.04-0.16 ng/mL
Species
Human
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
GeneID
3593(IL-12B) & 3592(IL-12A)
Accession
P29460(IL-12B) & P29459(IL-12A)
验证数据展示
Technical Specifications
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin Level | <1.0 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Biological Activity |
Measured by its ability to induce IFN-gamma secretion in human natural killer lymphoma NK-92 cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.04-0.16 ng/mL. |
| Source | HEK293-derived Human IL-12 protein Ile23-Ser328 (Human IL-12B Accession# P29460)+linker+Arg23-Ser219 (Human IL-12A Accession# P29459) with His tag at the C-terminus. |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 59.5 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 65-80 kDa |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Interleukin-12 (IL-12), is a cytokine that is secreted by activated phagocytes and dendritic cells and that induces interferon-γproduction by natural-killer and T lymphocytes. IL-12 (referred to as 'p70') is a 70 kDa heterodimer composed of a 35 kDa subunit (IL-12A p35) and a 40 kDa subunit (IL-12B p40). IL-12 is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. IL-12 also has anti-angiogenic activity, which means it can block the formation of new blood vessels. IL-12 has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of a variety of immune-related diseases.
References:
1. Picard C. et al. (2002). Am J Hum Genet.70: 336-48. 2. Randolph AG. et al. (2004). Am J Hum Genet. 75: 709-15. 3. Hsieh CS. et al. (1993). Science.260: 547-9. 4. Stern AS. et al.(1996). Life Sci. 58: 639-54. 5. Colombo MP. et al. (2002). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13: 155-68.